Corneal lenticule storage before reimplantation
- PMID: 29123364
- PMCID: PMC5661854
Corneal lenticule storage before reimplantation
Abstract
Purpose: To explore the optimal lenticule storage conditions that maintain lenticule integrity and clarity.
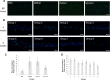
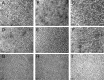
Methods: A total of 99 lenticules obtained from myopic patients undergoing small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) were divided into four combinations for short-term storage conditions: PBS, Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM), Optisol GS, or anhydrous glycerol. Two thirds of the lenticules were further stored for 4 weeks under eight different conditions. Clarity evaluation with transmittance measurements, cell-death assays with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated nick end labeling assay (TUNEL), collagen fibril spacing and necrotic response assessed with transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and immunohistochemistry analysis for human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) and CD45 for immunogenicity, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 for keratocyte response, were undertaken at baseline, 48 h (short term), and 4 weeks (long term).
Results: The TUNEL and immunogenicity results were comparable among the groups. The mean percentage of TUNEL-positive cells across all groups was 24.3% ± 11.8% and 62.9% ± 20.7% at the 48 h and 4 week time points, respectively. HLA-ABC+, HLA-DR+, and CD45+ cells were extremely rare, and MMP-2 expression ranged from non-detectable to minimal, under all conditions at all time points. Transmittance at 4 weeks was significantly different among groups with the greatest maintenance of clarity seen in the lenticules stored initially in DMEM at 4 °C for 48 h followed by cryopreservation in serum-free medium or glycerol at 4 °C followed by storage at room temperature. At TEM analysis at 4 weeks, the lenticules cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen, regardless of storage solutions, had significantly narrower inter-fibrillar distance than controls, while glycerol-preserved lenticules, at either room temperature or -80 °C, maintained the inter-fibrillar distance.
Conclusions: Clarity, structural integrity, and low immunogenicity under various conditions, at 4 °C or room temperature for short-term storage, offer encouragement for lenticule storage. It can be undertaken without access to s specialized and potentially expensive laboratory setup at least within the first 48 h before transportation to larger facilities for long-term storage.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Preservation of corneal stromal lenticule: review.Cell Tissue Bank. 2022 Dec;23(4):627-639. doi: 10.1007/s10561-021-09990-0. Epub 2022 Feb 6. Cell Tissue Bank. 2022. PMID: 35124756 Review.
-
Comparison of the Effects of Temperature and Dehydration Mode on Glycerin-Based Approaches to SMILE-Derived Lenticule Preservation.Cornea. 2022 Apr 1;41(4):470-477. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000002846. Cornea. 2022. PMID: 35244627 Free PMC article.
-
Cornea lenticule viability and structural integrity after refractive lenticule extraction (ReLEx) and cryopreservation.Mol Vis. 2011;17:3437-49. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22219639 Free PMC article.
-
Optical transmittance and ultrastructure of SMILE-derived lenticules subjected to three different preservative methods.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Dec;201:108357. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108357. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 33197451
-
The Preservation and Reuse of Lenticules Extracted via Small Incision Lenticule Extraction (SMILE): A Narrative Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Apr 3;12(4):380. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12040380. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preservation of corneal stromal lenticule: review.Cell Tissue Bank. 2022 Dec;23(4):627-639. doi: 10.1007/s10561-021-09990-0. Epub 2022 Feb 6. Cell Tissue Bank. 2022. PMID: 35124756 Review.
-
Corneal Donation: Current Guidelines and Future Direction.Clin Ophthalmol. 2021 Jul 12;15:2963-2973. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S284617. eCollection 2021. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34285462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human SMILE-Derived Stromal Lenticule Scaffold for Regenerative Therapy: Review and Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 19;23(14):7967. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147967. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Culture of Primary Neurons from Dissociated and Cryopreserved Mouse Trigeminal Ganglion.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2023 Aug;29(8):381-393. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2023.0054. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2023. PMID: 37212303 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal stromal dehydration and optimal stromal exposure time during corneal refractive surgery measured using a three-dimensional optical profiler.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022 Dec;260(12):4005-4013. doi: 10.1007/s00417-022-05764-w. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35876884
References
-
- Sekundo W, Kunert K, Russmann C, Gille A, Bissmann W, Stobrawa G, Sticker M, Bischoff M, Blum M. First efficacy and safety study of femtosecond lenticule extraction for the correction of myopia: six-month results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:1513–20. - PubMed
-
- Liu YC, Riau AK, Mehta JS. Small Incision Lenticule Extraction (SMILE). In: Krachmer JH, Mannis MJ, Holland EJ, editors. Cornea. 4th Edn. Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby: 2016. p. 1823–28.
-
- Sekundo W, Kunert KS, Blum M. Small incision corneal refractive surgery using the small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) procedure for the correction of myopia and myopic astigmatism: results of a 6 month prospective study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011;95:335–9. - PubMed
-
- Tan DK, Tay WT, Chan C, Tan DT, Mehta JS. Postoperative ocular higher-order aberrations and contrast sensitivity: femtosecond lenticule extraction versus pseudo small-incision lenticule extraction. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015;41:623–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

