Development of β-cyclodextrin-based hydrogel microparticles for solubility enhancement of rosuvastatin: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation
- PMID: 29123380
- PMCID: PMC5661467
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S143712
Development of β-cyclodextrin-based hydrogel microparticles for solubility enhancement of rosuvastatin: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation
Abstract
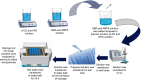
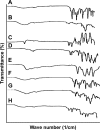
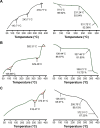
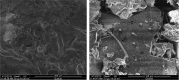
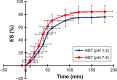
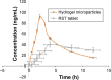
The aim of this study was to enhance the solubility of rosuvastatin (RST) calcium by developing β-cyclodextrin-g-poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid [AMPS]) hydrogel microparticles through aqueous free-radical polymerization technique. Prepared hydrogel microparticles were characterized for percent entrapment efficiency, solubility studies, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, thermal gravimetric analysis, powder X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, zeta size and potential, swelling and release studies. Formulations (HS1-HS9) have shown entrapment efficiency between 83.50%±0.30% and 88.50%±0.25%, and optimum release was offered by formulation HS7 at both pH levels, ie, 1.2 (89%) and 7.4 (92%). The majority of microparticles had a particle size of less than 500 µm and zeta potential of -37 mV. Similarly, optimum solubility, ie, 10.66-fold, was determined at pH 6.8 as compared to pure RST calcium, ie, 7.30-fold. In vivo studies on fabricated hydrogel microparticulate system in comparison to pure drug were carried out, and better results regarding pharmacokinetic parameters were seen in the case of hydrogel microparticles. A potential approach for solubility enhancement of RST calcium and other hydrophobic moieties was successfully developed.
Keywords: hydrogel microparticles; polymerization; rosuvastatin calcium; β-cyclodextrin solubility.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Development of β-cyclodextrin/polyvinypyrrolidone-co-poly (2-acrylamide-2-methylpropane sulphonic acid) hybrid nanogels as nano-drug delivery carriers to enhance the solubility of Rosuvastatin: An in vitro and in vivo evaluation.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 21;17(1):e0263026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263026. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35061861 Free PMC article.
-
FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF ACYCLOVIR LOADED POLYMERIC MICROPARTICLES: A SOLUBILITY ENHANCEMENT STUDY.Acta Pol Pharm. 2016 Sep;73(5):1311-1324. Acta Pol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 29638071
-
Novel multiparticulate pH triggered delayed release chronotherapeutic drug delivery of celecoxib-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes by using Box-Behnken design.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Apr 15;146:105254. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105254. Epub 2020 Feb 2. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32023488
-
Topical hydrogel matrix loaded with Simvastatin microparticles for enhanced wound healing activity.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017 Mar 1;72:160-167. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.11.038. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 28024572
-
Porous and highly responsive cross-linked β-cyclodextrin based nanomatrices for improvement in drug dissolution and absorption.Life Sci. 2021 Feb 15;267:118931. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118931. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33359243
Cited by
-
Directly compressed rosuvastatin calcium tablets that offer hydrotropic and micellar solubilization for improved dissolution rate and extent of drug release.Saudi Pharm J. 2019 Jul;27(5):619-628. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 May 8. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 31297015 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Optimization of Tamarind Gum-β-Cyclodextrin-g-Poly(Methacrylate) pH-Responsive Hydrogels for Sustained Delivery of Acyclovir.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 8;15(12):1527. doi: 10.3390/ph15121527. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36558978 Free PMC article.
-
Novel poly-β-cyclodextrin derivatives as advanced carriers for 5-fluorouracil for tumor: the impact of charge on antitumor efficiency.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Aug;9(8):4596-4606. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1118. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117824 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Statistically Optimized Chemically Cross-Linked Hydrogel for the Sustained-Release Delivery of Favipiravir.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 11;14(12):2369. doi: 10.3390/polym14122369. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745945 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, In Vitro Characterization, and Evaluation of Polymeric pH-Responsive Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Release.ACS Omega. 2024 Feb 19;9(9):10498-10516. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08107. eCollection 2024 Mar 5. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38463273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perrut M, Jung J, Leboeuf F. Enhancement of dissolution rate of poorly-soluble active ingredients by supercritical fluid processes: part I: micronization of neat particles. Int J Pharm. 2005;288(1):3–10. - PubMed
-
- Ku MS, Dulin W. A biopharmaceutical classification-based Right-First-Time formulation approach to reduce human pharmacokinetic variability and project cycle time from First-In-Human to clinical proof of concept. Pharm Dev Technol. 2012;17(3):285–305. - PubMed
-
- Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;23:3–25. - PubMed
-
- Hiroaki KUBO, Osawa T, Takashima K, Mizobe K. Enhancement of oral bioavailability and pharmacological effect of 1-(3, 4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2, 3-bis (methoxycarbonyl)-4-hydroxy-6, 7, 8-trimethoxynaphthalene (TA-7552), a new hypocholesterolemic agent, by micronization in co-ground mixture with D-mannitol. Biol Pharm Bull. 1996;19:741–747. - PubMed
-
- Martis L, Hall NA, Thakkar AL. Micelle formation and testosterone solubilization by sodium glycocholate. J Pharm Sci. 1972;61(11):1757–1761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

