Suppression of Inflammatory Demyelinaton and Axon Degeneration through Inhibiting Kv3 Channels
- PMID: 29123469
- PMCID: PMC5662905
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00344
Suppression of Inflammatory Demyelinaton and Axon Degeneration through Inhibiting Kv3 Channels
Abstract
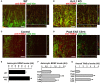
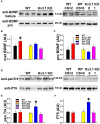
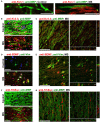
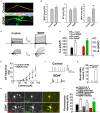
The development of neuroprotective and repair strategies for treating progressive multiple sclerosis (MS) requires new insights into axonal injury. 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), a blocker of voltage-gated K+ (Kv) channels, is used in symptomatic treatment of progressive MS, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Here we report that deleting Kv3.1-the channel with the highest 4-AP sensitivity-reduces clinical signs in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a mouse model for MS. In Kv3.1 knockout (KO) mice, EAE lesions in sensory and motor tracts of spinal cord were markedly reduced, and radial astroglia were activated with increased expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Kv3.3/Kv3.1 and activated BDNF receptors were upregulated in demyelinating axons in EAE and MS lesions. In spinal cord myelin coculture, BDNF treatment promoted myelination, and neuronal firing via altering channel expression. Therefore, suppressing Kv3.1 alters neural circuit activity, which may enhance BNDF signaling and hence protect axons from inflammatory insults.
Keywords: 4-aminopyridine; brain derived neurotrophic factor; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; multiple sclerosis; radial astroglia; voltage-gated K+ channel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
K+ Channel Kv3.4 Is Essential for Axon Growth by Limiting the Influx of Ca2+ into Growth Cones.J Neurosci. 2017 Apr 26;37(17):4433-4449. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1076-16.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 20. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28320840 Free PMC article.
-
[Ion channels and demyelination: basis of a treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) by potassium channel blockers].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2004 May;160(5 Pt 2):S16-27. doi: 10.1016/s0035-3787(04)71001-2. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2004. PMID: 15269656 French.
-
K+ channel alterations in the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Aug;47(2):280-93. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.04.012. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 22560931 Free PMC article.
-
Nudging oligodendrocyte intrinsic signaling to remyelinate and repair: Estrogen receptor ligand effects.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Jun;160:43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Jan 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26776441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of axonal dysfunction after spinal cord injury: with an emphasis on the role of voltage-gated potassium channels.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001 Dec;38(1-2):165-91. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(01)00134-5. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11750932 Review.
Cited by
-
Immediate induction of varicosities by transverse compression but not uniaxial stretch in axon mechanosensation.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Jan 24;10(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01309-8. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35074017 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Properties of 4-Aminopyridine.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021 Mar 2;8(3):e976. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000976. Print 2021 May. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021. PMID: 33653963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4-aminopyridine is not just a symptomatic therapy, it has a neuroprotective effect - Yes.Mult Scler. 2020 Oct;26(11):1309-1310. doi: 10.1177/1352458520923951. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Mult Scler. 2020. PMID: 32628062 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Wireless Localized Electrical Stimulation Generated by an Ultrasound-Driven Piezoelectric Discharge Regulates Proinflammatory Macrophage Polarization.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 May 3;8(13):2100962. doi: 10.1002/advs.202100962. eCollection 2021 Jul. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34258169 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanical Microenvironment Regulates Axon Diameters Visualized by Cryo-Electron Tomography.Cells. 2022 Aug 15;11(16):2533. doi: 10.3390/cells11162533. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brew H. M., Gittelman J. X., Silverstein R. S., Hanks T. D., Demas V. P., Robinson L. C., et al. . (2007). Seizures and reduced life span in mice lacking the potassium channel subunit Kv1.2, but hypoexcitability and enlarged Kv1 currents in auditory neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 98, 1501–1525. 10.1152/jn.00640.2006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cameron M. H., Fitzpatrick M., Overs S., Murchison C., Manning J., Whitham R. (2014). Dalfampridine improves walking speed, walking endurance, and community participation in veterans with multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal cohort study. Mult. Scler. 20, 733–738. 10.1177/1352458513507356 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

