Toll-Like Receptor Ligands and Interferon-γ Synergize for Induction of Antitumor M1 Macrophages
- PMID: 29123526
- PMCID: PMC5662546
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01383
Toll-Like Receptor Ligands and Interferon-γ Synergize for Induction of Antitumor M1 Macrophages
Abstract
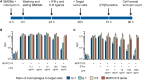
Tumor-associated macrophages may either promote or suppress tumor growth depending on their activation status. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) has been identified as a key factor for inducing tumoricidal M1 phenotype in macrophages. However, it remains unclear whether IFN-γ is sufficient or if additional stimuli are required. Here, we tested IFN-γ and a panel of toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists for the ability to activate murine macrophages toward a tumoricidal M1 phenotype. The following TLR ligands were used: TLR1/TLR2 agonist Pam3CSK4, TLR2/TLR6 agonist lipotechoic acid, TLR3 agonist poly(I:C), TLR4 agonist lipopolysaccharide (LPS), TLR5 agonist flagellin, TLR7 agonist CL264, and TLR9 agonist CpG. We used an in vitro growth inhibition assay to measure both cytotoxic and cytostatic activity of mouse macrophages against Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) and MOPC315 plasmacytoma tumor cells. Production of nitric oxide (NO) and cytokines by activated macrophages was quantified. We found that IFN-γ alone was not able to render macrophages tumoricidal. Similarly, macrophage activation with single TLR agonists was inefficient. In sharp contrast, IFN-γ was shown to synergize with TLR agonists for induction of macrophage tumoricidal activity and production of both NO and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-12p40, and IL-12p70). Furthermore, IFN-γ was shown to suppress macrophage IL-10 secretion induced by TLR agonists. NO production was necessary for macrophage tumoricidal activity. We conclude that two signals from the microenvironment are required for optimal induction of antitumor M1 macrophage phenotype. Combination treatment with IFN-γ and TLR agonists may offer new avenues for macrophage-based cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: cancer; immunotherapy; interferon-γ; macrophages; nitric oxide; toll-like receptors; tumoricidal.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

