Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome: more than a FAScinating disease
- PMID: 29123652
- PMCID: PMC5668920
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.11545.1
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome: more than a FAScinating disease
Abstract
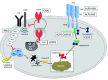
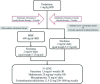
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) is an inherited syndrome characterized by abnormal lymphocyte survival caused by failure of apoptotic mechanisms to maintain lymphocyte homeostasis. This failure leads to the clinical manifestations of non-infectious and non-malignant lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and autoimmune pathology, most commonly, autoimmune cytopenias. Since ALPS was first characterized in the early 1990s, insights in disease biology have improved both diagnosis and management of this syndrome. Sirolimus is the best-studied and most effective corticosteroid-sparing therapy for ALPS and should be considered first-line for patients in need of chronic treatment. This review highlights practical clinical considerations for the diagnosis and management of ALPS. Further studies could reveal new proteins and regulatory pathways that are critical for lymphocyte activation and apoptosis.
Keywords: Fas/FasL; MMF; Targeted therapy; autoimmune; cytopenias; double negative T cells; lymphoproliferative disease; sirolimus.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Teachey DT: Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome: new approaches to diagnosis and management. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2011;9(3):233–5. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

