Life-threatening urethral hemorrhage after placement of a Foley catheter in a patient with uroseptic disseminated intravascular coagulation due to chronic urinary retention induced by untreated benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 29123824
- PMCID: PMC5667313
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.209
Life-threatening urethral hemorrhage after placement of a Foley catheter in a patient with uroseptic disseminated intravascular coagulation due to chronic urinary retention induced by untreated benign prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
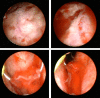
Case: A 77-year-old man with severe septic disseminated intravascular coagulation following urinary infection was transported to our hospital. He had developed urinary retention induced by untreated prostatic hyperplasia. Immediate drainage with a Foley catheter was successfully carried out, but the hematuria progressed to life-threatening hemorrhage.
Outcome: Complete hemostasis was impossible by surgical treatment because the tissue around the prostatic urethra was very fragile and hemorrhagic. Organized treatments (continuous hemodiafiltration combined with polymyxin-B immobilized fiber column hemoperfusion and systemic treatment with antibiotics and coagulation factors) were commenced soon after the operation. The patient eventually recovered from the septic disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Conclusion: This case report illustrates the risk of placement of Foley catheters in patients with severe septic disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Keywords: Benign prostatic hyperplasia; PMX; chronic urinary retention; septic DIC; urethral hemorrhage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of Point-of-Care Ultrasound to Facilitate Guidance and Intrauterine Placement of a Foley Urinary Catheter to Tamponade Life-Threatening Postprocedure Hemorrhage Caused by Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation.J Emerg Med. 2020 Feb;58(2):e75-e78. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2019.11.033. Epub 2020 Jan 22. J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 31982201
-
Effective combination therapy of polymyxin-B direct hemoperfusion and recombinant thrombomodulin for septic shock accompanied by disseminated intravascular coagulation: a historical controlled trial.Ther Apher Dial. 2013 Oct;17(5):472-6. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.12112. Ther Apher Dial. 2013. PMID: 24107274
-
Successful treatments with polymyxin B hemoperfusion and recombinant human thrombomodulin for fulminant Clostridium difficile-associated colitis with septic shock and disseminated intravascular coagulation: a case report.Surg Case Rep. 2016 Dec;2(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s40792-016-0199-5. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Surg Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27468959 Free PMC article.
-
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation.Am J Clin Pathol. 2016 Dec;146(6):670-680. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqw195. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Am J Clin Pathol. 2016. PMID: 28013226 Review.
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986 Dec;8(6 Suppl B):159B-167B. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(86)80017-1. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986. PMID: 3537068 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary Tract Infections and Associated Factors among Patients with Indwelling Urinary Catheters Attending Bugando Medical Centre a Tertiary Hospital in Northwestern Tanzania.Microorganisms. 2022 Feb 21;10(2):473. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020473. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Igawa Y, Wyndaele JJ, Nishizawa O. Catheterization: possible complications and their prevention and treatment. Int. J. Urol. 2008; 15: 481–5. - PubMed
-
- Hollingsworth JM, Rogers MA, Krein SL et al Determining the noninfectious complications of indwelling urethral catheters: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013; 159: 401–10. - PubMed
-
- Sklar DP, Diven B, Jones J. Incidence and magnitude of catheter‐induced hematuria. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1986; 4: 14–6. - PubMed
-
- Liu JJ, Guo DP, Gill H. Patterns of urinary catheter consults in a tertiary care hospital. Can J Urol. 2013; 20: 7046–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

