Delayed massive epistaxis from traumatic intracranial aneurysm after blunt facial injury
- PMID: 29123850
- PMCID: PMC5667291
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.239
Delayed massive epistaxis from traumatic intracranial aneurysm after blunt facial injury
Abstract
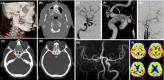
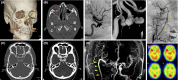
Cases: Traumatic intracranial aneurysm following blunt head injury is uncommon but can be induced by extension of skull base fracture and causes unexpected hemorrhagic complications. We present two cases of traumatic intracranial aneurysm in the paraclinoid area that was revealed by delayed massive epistaxis. Lack of initial neurological deficits omitted screening for cerebrovascular injury.
Outcome: Internal trapping was carried out using endovascular techniques in both cases, with extracranial-intracranial bypass in one case. No recurrent bleeding occurred in either case.
Conclusion: To prevent unexpected delayed life-threatening hemorrhagic accidents, careful assessment of skull-base fracture is prerequisite, even in cases of mild facial injury.
Keywords: Blunt facial injury; endovascular trapping; extracranial–intracranial bypass; massive epistaxis; traumatic intracranial aneurysm.
Figures
References
-
- Emmett KP, Fabian TC, DiCocco JM, Zarzaur BL, Croce MA. Improving the screening criteria for blunt cerebrovascular injury: the appropriate role for computed tomography angiography. J. Trauma 2011; 70: 1058–65. - PubMed
-
- Hughes KM, Collier B, Greene KA, Kurek S. Traumatic carotid artery dissection: a significant incidental finding. Am. Surg. 2000; 66: 1023–7. - PubMed
-
- Komiyama M, Morikawa T, Nakajima H, Yasui T, Kan M. “Early” apoplexy due to traumatic intracranial aneurysm–case report. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2001; 41: 264–70. - PubMed
-
- Dubey A, Sung WS, Chen YY et al Traumatic intracranial aneurysm: a brief review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008; 15: 609–12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

