Management of maternal anaphylaxis in pregnancy: a case report
- PMID: 29123862
- PMCID: PMC5667276
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.238
Management of maternal anaphylaxis in pregnancy: a case report
Abstract
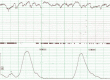
Case: A 26-year-old woman (gravida 2, para 1) at 25 weeks' gestation was brought to the emergency department because of anaphylactic symptoms. She reported eating Japanese soba and developed symptoms of dyspnea, generalized itchy rash, abdominal pain, and severe uterine contractions within 15-30 min of eating. She was immediately treated by normal saline infusion, two injections of epinephrine (intramuscularly), and a nebulized short-acting β2-receptor agonist, followed by H1-antihistamine and methylprednisolone. Obstetrical management was undertaken by an obstetrician.
Outcome: The patient recovered rapidly without a biphasic reaction of anaphylaxis. After 11 weeks, a healthy, neurologically intact baby was born.
Conclusion: Management of anaphylaxis in pregnant patients is basically the same of that in non-pregnant ones. Treatment should commence immediately to prevent further development of the anaphylaxis reaction and fetal neurological deficiency.
Keywords: Anaphylactic shock; fetal brain damage; fetal distress; food allergy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal anaphylactic shock in pregnancy: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Sep;97(37):e12351. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012351. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30212990 Free PMC article.
-
Guidelines for the Management of a Pregnant Trauma Patient.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015 Jun;37(6):553-74. doi: 10.1016/s1701-2163(15)30232-2. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015. PMID: 26334607 English, French.
-
Beta-2 Agonists May be Superior to Epinephrine to Relieve Severe Anaphylactic Uterine Contractions.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 Mar;9(3):1232-1241. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.10.047. Epub 2020 Nov 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021. PMID: 33181341
-
Anaphylactic shock in pregnancy: a case study and review of the literature.Int J Obstet Anesth. 2008 Oct;17(4):350-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2008.05.002. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2008. PMID: 18691872 Review.
-
[A case study of anaphylaxis in a pregnant woman].Ginecol Obstet Mex. 2014 Mar;82(3):188-93. Ginecol Obstet Mex. 2014. PMID: 24779274 Spanish.
Cited by
-
State-of-the-Art on Biomarkers for Anaphylaxis in Obstetrics.Life (Basel). 2021 Aug 24;11(9):870. doi: 10.3390/life11090870. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34575019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mastocytosis: Fertility and Pregnancy Management in a Rare Disease.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 27;12:874178. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.874178. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35574357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anaphylaxis-induced premature uterine contractions: a case report and literature review.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Mar 13;24(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06297-2. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38481196 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mulla ZD, Ebrahim MS, Gonzalez JL. Anaphylaxis in the obstetric patient: analysis of a statewide hospital discharge database. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010; 104: 55–9. - PubMed
-
- Simons FER, Schatz M. Anaphylaxis during pregnancy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012; 130: 597–606. - PubMed
-
- Berardi A, Rossi K, Cavalleri F, et al Maternal anaphylaxis and fetal brain damage after intrapartum chemoprophylaxis. J. Perinat. Med. 2004; 32: 375–7. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri K, Gonzales J, Jesrun CA, Ambat MT, Mandal‐Chaudhuri S. Anaphylactic shock in pregnancy: a case study and review of the literature. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2009; 17: 350–7. - PubMed
-
- Berenguer A, Couto A, Brites V, Fernandes R. Anaphylaxis in pregnancy: a rare cause of neonatal mortality. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007055. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3603634/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources