Drug-induced anaphylaxis in the emergency room
- PMID: 29123869
- PMCID: PMC5674474
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.282
Drug-induced anaphylaxis in the emergency room
Abstract
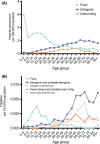
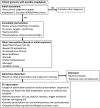
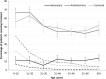
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening, systemic allergic reaction that presents unique challenges for emergency care practitioners. Anaphylaxis occurs more frequently than previously believed. Therefore, proper knowledge regarding the epidemiology, mechanisms, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of anaphylaxis is essential. In particular, the initial treatment strategy, followed by correct diagnosis, in the emergency room is critical for preventing fatal anaphylaxis, although making a diagnosis is not easy because of the broad and often atypical presentation of anaphylaxis. To this end, the clinical criteria proposed by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network are useful, which, together with a differential diagnosis, could enable a more accurate diagnosis. Additional in vitro tests, such as plasma histamine and tryptase measurements, are also helpful. It should be emphasized that adrenaline is the only drug recommended as first-line therapy in all published national anaphylaxis guidelines. Most international anaphylaxis guidelines recommend injecting adrenaline by the intramuscular route in the mid-anterolateral thigh, whereas i.v. adrenaline is an option for patients with severe hypotension or cardiac arrest unresponsive to intramuscular adrenaline and fluid resuscitation. In addition to the route of administration, choosing the appropriate dose of adrenaline is essential, because serious adverse effects can potentially occur after an overdose of adrenaline. Furthermore, to avoid future recurrence of anaphylaxis, providing adrenaline auto-injectors and making an etiological diagnosis, including confirmation of the offending trigger, are recommended for patients at risk of anaphylaxis before their discharge from the emergency room.
Keywords: Cardiopulmonary arrest; emergency room; shock.
Figures


References
-
- Sampson HA, Munoz‐Furlong A, Campbell RL et al Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report–Second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006; 117: 391–7. - PubMed
-
- Klein JS, Yocum MW. Underreporting of anaphylaxis in a community emergency room. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995; 95: 637–8. - PubMed
-
- Campbell RL, Hagan JB, Manivannan V et al Evaluation of national institute of allergy and infectious diseases/food allergy and anaphylaxis network criteria for the diagnosis of anaphylaxis in emergency department patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012; 129: 748–52. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez‐Perea A, Tomas‐Perez M, Martinez‐Lezcano P et al Anaphylaxis in adolescent/adult patients treated in the emergency department: differences between initial impressions and the definitive diagnosis. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2015; 25: 288–94. - PubMed
-
- Liew WK, Williamson E, Tang ML. Anaphylaxis fatalities and admissions in Australia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009; 123: 434–42. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

