Direct intrahepatic portocaval shunt for refractory hepatic hydrothorax: a case report
- PMID: 29123879
- PMCID: PMC5674466
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.257
Direct intrahepatic portocaval shunt for refractory hepatic hydrothorax: a case report
Abstract
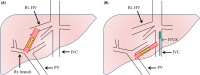
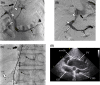
Case: A 64-year-old man with complaints of dyspnea and orthopnea secondary to a hepatic hydrothorax refractory to diuretic medication underwent the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure to decrease the portal vein pressure. The TIPS procedure failed due to severe liver stiffness. Direct intrahepatic portocaval shunt (DIPS), a modified TIPS procedure that directly inserts a stent from the inferior vena cava to the portal vein, was successfully carried out.
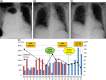
Outcome: The DIPS procedure significantly decreased the patient's pleural effusion and respiratory symptoms.
Conclusion: No other medical treatment is available to control refractory pleural effusion caused by portal hypertension; however, the TIPS (or DIPS) procedure can be successfully carried out in patients <60 years old with a Model of End-Stage Liver Disease score <15.
Keywords: Ascites; hypertension, portal; liver cirrhosis; pleural effusion; portosystemic shunt, transjugular intrahepatic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transjugular liver biopsy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) or direct intrahepatic portocaval shunt (DIPS): Is it feasible, effective, and safe?Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018 May;99(5):331-335. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2017.12.012. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29366793
-
Transsplenic portal vein recanalization and direct intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement to optimize liver transplantation.CVIR Endovasc. 2020 Jan 8;3(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s42155-019-0096-7. CVIR Endovasc. 2020. PMID: 32026045 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and long-term hemodynamic effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: a Doppler/manometric correlative study.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995 Apr;164(4):997-1002. doi: 10.2214/ajr.164.4.7726065. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995. PMID: 7726065
-
[TIPS - Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. A review].Arq Gastroenterol. 2001 Jan-Mar;38(1):69-80. doi: 10.1590/s0004-28032001000100013. Arq Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11586999 Review. Portuguese.
-
Recent position of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the treatment of portal hypertension.Hepatogastroenterology. 1997 May-Jun;44(15):647-55. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997. PMID: 9222665 Review.
References
-
- Siddappa PK, Kar P. Hepatic hydrothorax. Trop. Gastroenterol. 2009; 30: 135–41. - PubMed
-
- Rössle M. TIPS: 25 years later. J. Hepatol. 2013; 59: 1081–93. - PubMed
-
- Fidelman N, Kwan SW, LaBerge JM, Gordon RL, Ring EJ, Kerlan RK Jr. The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: an update. Am. J. Roentogenol. 2012; 199: 746–55. - PubMed
-
- Kirby JM, Cho KJ, Midia M. Image‐guided intervention in management of complications of portal hypertension: more than TIPS for success. Radiographics 2013; 33: 1473–96. - PubMed
-
- Boyer TD, Haskal ZJ. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guidelines: the role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in the management of portal hypertension. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2005; 16: 615–29. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

