Locus Coeruleus and Dopamine-Dependent Memory Consolidation
- PMID: 29123927
- PMCID: PMC5662828
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8602690
Locus Coeruleus and Dopamine-Dependent Memory Consolidation
Abstract
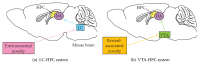
Most everyday memories including many episodic-like memories that we may form automatically in the hippocampus (HPC) are forgotten, while some of them are retained for a long time by a memory stabilization process, called initial memory consolidation. Specifically, the retention of everyday memory is enhanced, in humans and animals, when something novel happens shortly before or after the time of encoding. Converging evidence has indicated that dopamine (DA) signaling via D1/D5 receptors in HPC is required for persistence of synaptic plasticity and memory, thereby playing an important role in the novelty-associated memory enhancement. In this review paper, we aim to provide an overview of the key findings related to D1/D5 receptor-dependent persistence of synaptic plasticity and memory in HPC, especially focusing on the emerging evidence for a role of the locus coeruleus (LC) in DA-dependent memory consolidation. We then refer to candidate brain areas and circuits that might be responsible for detection and transmission of the environmental novelty signal and molecular and anatomical evidence for the LC-DA system. We also discuss molecular mechanisms that might mediate the environmental novelty-associated memory enhancement, including plasticity-related proteins that are involved in initial memory consolidation processes in HPC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Locus coeruleus and dopaminergic consolidation of everyday memory.Nature. 2016 Sep 15;537(7620):357-362. doi: 10.1038/nature19325. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27602521 Free PMC article.
-
Novelty and Dopaminergic Modulation of Memory Persistence: A Tale of Two Systems.Trends Neurosci. 2019 Feb;42(2):102-114. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Trends Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30455050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PV plasticity sustained through D1/5 dopamine signaling required for long-term memory consolidation.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Mar;19(3):454-64. doi: 10.1038/nn.4231. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26807952
-
Frequency-dependency of the involvement of dopamine D1/D5 and beta-adrenergic receptors in hippocampal LTD triggered by locus coeruleus stimulation.Hippocampus. 2022 Jun;32(6):449-465. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23419. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Hippocampus. 2022. PMID: 35478421
-
The Longevity of Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Is Orchestrated by the Locus Coeruleus-Noradrenergic System.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:2727602. doi: 10.1155/2017/2727602. Epub 2017 Jun 11. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 28695015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Locus coeruleus-CA1 projections are involved in chronic depressive stress-induced hippocampal vulnerability to transient global ischaemia.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 3;10(1):2942. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10795-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31270312 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of memory modulation by conditioned stimuli.Learn Mem. 2021 Feb 16;28(3):87-94. doi: 10.1101/lm.052407.120. Print 2021 Mar. Learn Mem. 2021. PMID: 33593927 Free PMC article.
-
Entacapone promotes hippocampal neurogenesis in mice.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Jun;16(6):1005-1110. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.300447. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33269743 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct catecholaminergic pathways projecting to hippocampal CA1 transmit contrasting signals during navigation in familiar and novel environments.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 24:2023.11.29.569214. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.29.569214. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Nov 06;13:RP95213. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95213. PMID: 38076843 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Specific Hippocampal Interneurons Shape Consolidation of Recognition Memory.Cell Rep. 2020 Aug 18;32(7):108046. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108046. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32814049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown R., Kulik J. Flashbulb memories. Cognition. 1977;5(1):73–99. doi: 10.1016/0010-0277(77)90018-x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

