Ionizing radiation sensitizes tumors to PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade in orthotopic murine head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 29123967
- PMCID: PMC5665079
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1356153
Ionizing radiation sensitizes tumors to PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade in orthotopic murine head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
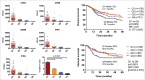
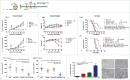
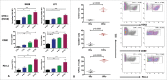
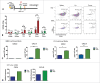
Immunotherapy clinical trials targeting the programmed-death ligand axis (PD-1/PD-L1) show that most head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients are resistant to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition. We investigated whether local radiation to the tumor can transform the immune landscape and render poorly immunogenic HNSCC tumors sensitive to PD-L1 inhibition. We used the first novel orthotopic model of HNSCC with genetically distinct murine cell lines. Tumors were resistant to PD-L1 checkpoint blockade, harbored minimal PD-L1 expression and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes at baseline, and were resistant to radiotherapy. The combination of radiation and PD-L1 inhibition significantly enhanced tumor control and improved survival. This was mediated in part through upregulation of PD-L1 on tumor cells and increased T-cell infiltration after RT, resulting in a highly inflamed tumor. Depletion of both CD4 and CD8 T-cells completely abrogated the effect of anti PD-L1 with radiation on tumor growth. Our findings provide evidence that radiation to the tumor can induce sensitivity to PD-L1 checkpoint blockade in orthotopic models of HNSCC. These findings have direct relevance to high risk HNSCC patients with poorly immunogenic tumors and who may benefit from combined radiation and checkpoint blockade.
Keywords: PD-L1; Radiotherapy; head and neck cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Figures

References
-
- Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(14):2137-50. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.05.2308. PMID:16682732 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Taube JM, Klein A, Brahmer JR, Xu H, Pan X, Kim JH, Chen L, Pardoll DM, Topalian SL, Anders RA. Association of PD-1, PD-1 ligands, and other features of the tumor immune microenvironment with response to anti-PD-1 therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(19):5064-74. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3271. PMID:24714771 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Topalian SL, Sznol M, McDermott DF, Kluger HM, Carvajal RD, Sharfman WH, Brahmer JR, Lawrence DP, Atkins MB, Powderly JD, et al.. Survival, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(10):1020-30. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.53.0105. PMID:24590637 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li H, Chiappinelli KB, Guzzetta AA, Easwaran H, Yen RW, Vatapalli R, Topper MJ, Luo J, Connolly RM, Azad NS, et al.. Immune regulation by low doses of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-azacitidine in common human epithelial cancers. Oncotarget. 2014;5(3):587-98. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.1782. PMID:24583822 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
