Rare complicated parapneumonic effusion, Mycoplasma pneumoniae with new-onset lupus flare: Case report and literature review
- PMID: 29124008
- PMCID: PMC5671404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2017.10.010
Rare complicated parapneumonic effusion, Mycoplasma pneumoniae with new-onset lupus flare: Case report and literature review
Abstract
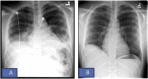
Mycoplasma pneumoniae has been associated with respiratory tract infections. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia-related pleural effusion is rarely reported. Extra-pulmonary abnormalities such as encephalitis, myocarditis, glomerulonephritis, and myringitis have been reported. However pulmonary manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus include pneumonitis, pleurisy, interstitial lung disease, and thromboembolic disease. We present the case of a 26-year-old male who came for evaluation of fever, cough, and shortness of breath with right-sided chest pain. He was found to have right-side loculated complicated parapneumonic effusion and underwent drainage with a pleural catheter followed by fibrinolytic therapy. He was then found to have new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus concomitant with Mycoplasma pneumonia, leading to lupus flare and lupus nephritis. He responded well to levofloxacin, steroids, hydroxychloroquine, and mycophenolate, with complete resolution of loculated pleural effusion and symptom improvement. Our case describes the rare combination of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia, parapneumonic pleural effusion, and lupus flare with lupus nephritis. Early identification and treatment can lead to better out come in young patients.
Keywords: Lupus flare; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Parapneumonic effusion.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Massive parapneumonic effusion caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in a child: a case report].Tuberk Toraks. 2008;56(3):310-4. Tuberk Toraks. 2008. PMID: 18932033 Turkish.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting as pleural effusion: report of a case.J Formos Med Assoc. 1995 Dec;94(12):746-9. J Formos Med Assoc. 1995. PMID: 8541737
-
The Association Between Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae, a Life-Threatening Condition in Small Children-A Case Report and a Review of the Literature.Front Pediatr. 2020 Nov 10;8:558941. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.558941. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33240829 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the role of intrapleural fibrinolytic therapy in the management of complicated parapneumonic effusions and empyema.Acta Med Indones. 2012 Jul;44(3):258-64. Acta Med Indones. 2012. PMID: 22983084 Review.
-
[Using of fibrinolytics in the treatment of complicated parapneumonic effusion and empyema in children].Tuberk Toraks. 2003;51(3):320-4. Tuberk Toraks. 2003. PMID: 15143413 Review. Turkish.
Cited by
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pleural Effusion in Adults.J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 26;11(5):1281. doi: 10.3390/jcm11051281. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35268372 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clyde W.A., Jr. Clinical overview of typical Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1993 Aug;17(Suppl 1):S32–S36. - PubMed
-
- Narita M., Tanaka H. Two distinct patterns of pleural effusions caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004 Nov;23(11):1069. - PubMed
-
- Isenberg D.A., Allen E., Farewell V., D'Cruz D. An assessment of disease flare in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of BILAG 2004 and the flare version of SELENA. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011 Jan;70(1):54–59. - PubMed
-
- Machado A.A., Zorzi A.R., Gléria A.E. Frequency of Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma urealyticum infections in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2001 May-Jun;34(3):243–247. - PubMed
-
- Jansson E., Vainio U., Tuuri S. Cultivation of a mycoplasma from the bone marrowin systemic lupus erythematosus disseminatus. Acta Rheumatol. Scand. 1971;17(3):223–226. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

