Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: A Clinical Perspective
- PMID: 29124057
- PMCID: PMC5662579
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00066
Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: A Clinical Perspective
Abstract
Cancer survival has improved dramatically, and this has led to the manifestation of late side effects of multimodality therapy. Radiation (RT) to the thoracic malignancies results in unintentional irradiation of the cardiac chambers. RT-induced microvascular ischemia leads to disruption of capillary endothelial framework, and injury to differentiated myocytes results in deposition of collagen and fibrosis. Coexistence of risk factors of metabolic syndrome and preexisting atherosclerosis in addition to RT exposure results in accelerated occurrence of major coronary events. Hence, it becomes pertinent to understand the underlying pathophysiology and clinical manifestations of RT-induced cardiovascular disease to devise optimal preventive and surveillance strategies.
Keywords: biomarkers; cancer; cardiovascular disease; ischemic heart disease; radiation.
Figures
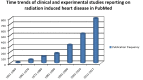
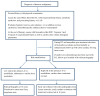
References
-
- WHO. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) (2017). Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

