Intrinsically disordered proteins in the nucleus of human cells
- PMID: 29124132
- PMCID: PMC5668563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.03.003
Intrinsically disordered proteins in the nucleus of human cells
Abstract
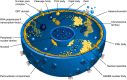
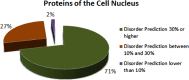
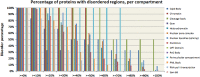
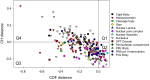
Intrinsically disordered proteins are known to perform a variety of important functions such as macromolecular recognition, promiscuous binding, and signaling. They are crucial players in various cellular pathway and processes, where they often have key regulatory roles. Among vital cellular processes intimately linked to the intrinsically disordered proteins is transcription, an intricate biological performance predominantly developing inside the cell nucleus. With this work, we gathered information about proteins that exist in various compartments and sub-nuclear bodies of the nucleus of the human cells, with the goal of identifying which ones are highly disordered and which functions are ascribed to the disordered nuclear proteins.
Keywords: Cell nucleus; Homo sapiens; Intrinsically disordered proteins; Nuclear compartments; Nuclear proteins; Protein function.
Figures
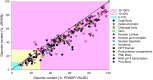



References
-
- Goodsell D.S. Miniseries: illustrating the machinery of life: eukaryotic cell panorama. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ.: Bimon. Publ. Int. Union Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011;39:91–101. - PubMed
-
- Tripathi V., Prasanth K.V. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; Chichester: 2011. Cell Nucleus. eLS.
-
- Hancock R., Jeon K., editors. Academic Press; Amsterdam, Boston, Heidelberg, London, New York, Oxford, Paris, San Diego, San Francisco, Singapoe, Sydney, Tokyo: 2014. New Models of the Cell Nucleus: Crowding, Entropic Forces, Phase Separation, and Fractals.
-
- Fakan S. The functional architecture of the nucleus as analysed by ultrastructural cytochemistry. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2004;122:83–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

