Construction of P-glycoprotein incorporated tethered lipid bilayer membranes
- PMID: 29124152
- PMCID: PMC5668657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.05.012
Construction of P-glycoprotein incorporated tethered lipid bilayer membranes
Abstract
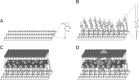
To investigate drug-membrane protein interactions, an artificial tethered lipid bilayer system was constructed for the functional integration of membrane proteins with large extra-membrane domains such as multi-drug resistance protein 1 (MDR1). In this study, a modified lipid (i.e., 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[amino (polyethylene glycol)-2000] (DSPE-PEG)) was utilized as a spacer molecule to elevate lipid membrane from the sensor surface and generate a reservoir underneath. Concentration of DSPE-PEG molecule significantly affected the liposome binding/spreading and lipid bilayer formation, and 0.03 mg/mL of DSPE-PEG provided optimum conditions for membrane protein integration. Further, the incorporation of MDR1 increased the local rigidity on the platform. Antibody binding studies showed the functional integration of MDR1 protein into lipid bilayer platform. The platform allowed to follow MDR!-statin-based drug interactions in vitro. Each binding event and lipid bilayer formation was monitored in real-time using Surface Plasmon Resonance and Quartz Crystal Microbalance-Dissipation systems, and Atomic Force Microscopy was used for visualization experiments.
Keywords: Drug–protein interactions; P-glycoprotein; Statins; Tethered lipid bilayer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Preparation of tethered-lipid bilayers on gold surfaces for the incorporation of integral membrane proteins synthesized by cell-free expression.Langmuir. 2014 Mar 25;30(11):3132-41. doi: 10.1021/la5004758. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Langmuir. 2014. PMID: 24568716
-
Synthesis and characterization of tethered lipid assemblies for membrane protein reconstitution (Review).Biointerphases. 2017 Sep 28;12(4):04E301. doi: 10.1116/1.4994299. Biointerphases. 2017. PMID: 28958150 Review.
-
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: a review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt A):427-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23872180 Review.
-
Controlling spatial distribution of functional lipids in a supported lipid bilayer prepared from vesicles.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Jun 15;664:1042-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2024.03.055. Epub 2024 Mar 11. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 38522178 Free PMC article.
-
A facile approach for assembling lipid bilayer membranes on template-stripped gold.Langmuir. 2010 Dec 7;26(23):18239-45. doi: 10.1021/la102774n. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Langmuir. 2010. PMID: 21050009
Cited by
-
In situ synthesis and dynamic simulation of molecularly imprinted polymeric nanoparticles on a micro-reactor system.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 10;14(1):4840. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40413-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37563147 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Biomimetic Systems for Molecular Recognition and Biosensing.Biomimetics (Basel). 2020 May 12;5(2):20. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics5020020. Biomimetics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32408710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-induced activation of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 leads to minor localized structural changes.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 12;14(4):e0214969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214969. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30978226 Free PMC article.
-
The complex relationship between multiple drug resistance and the tumor pH gradient: a review.Cancer Drug Resist. 2022 Apr 3;5(2):277-303. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2021.134. eCollection 2022. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35800371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer-Based Point-of-Care Devices: Emerging Technologies and Integration of Computational Methods.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 May 22;13(5):569. doi: 10.3390/bios13050569. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37232930 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnell R., Ferraz N., Fornstedt T. Analytical characterization of chiral drug–protein interactions: comparison between the optical biosensor (surface plasmon resonance) assay and the HPLC perturbation method. Anal. Chem. 2006;78(5):1682–1689. - PubMed
-
- Jackman J.A., Knoll W., Cho N.-J. Biotechnology applications of tethered lipid bilayer membranes. Materials. 2012;5(12):2637–2657.
-
- Lucio M., Ferreira H., Lima J.L.F.C., Reis S. Use of liposomes as membrane models to evaluate the contribution of drug–membrane interactions to antioxidant properties of etodolac. Redox Rep. 2008;13(5):225–236. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

