Catalase from larvae of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii
- PMID: 29124232
- PMCID: PMC5669351
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.09.023
Catalase from larvae of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii
Abstract
Catalase plays a major role in protecting cells against toxic reactive oxygen species. Here, Catalase was purified from larvae of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii and designated TLCAT. It was purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation and chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, Sephacryl S-300 and CM-cellulose columns. Gel filtration and SDS-PAGE of the purified TLCAT indicated that the protein has a native molecular weight of 120 kDa and is most likely a homodimer with a subunit of approximately 60 kDa. The Km value of TLCAT is 12 mM H2O2 and displayed its optimum activity at pH 7.2. CaCl2, MgCl2, MnCl2 and NiCl2 increased the activity of TLCAT, while FeCl2, CoCl2, CuCl2 and ZnCl2 inhibited the activity of TLCAT. Sodium azide inhibited TLCAT competitively with a Ki value of 0.28 mM. The presence of TLCAT in cells may play a role in protecting H. dromedarii ticks against oxidative damage. This finding will contribute to our understanding of the physiology of these ectoparasites and the development of untraditional methods to control them.
Keywords: BSA, bovine serum albumin; CAT, catalase; Camel tick; Catalase; Characterization; PAGE, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; Purification; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TLCAT, tick larvae catalase; larvae.
Figures
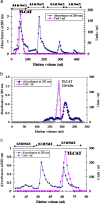


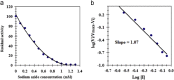
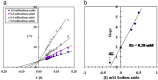
References
-
- Aebi H. Catalase in vitro Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Boon E.M., Downs A., Marcey D. Mechanism of catalase in hydrogen peroxide. Physiol. Rev. 1978;13 87-80.
-
- Bradford M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Barker S.C., Murrell A. Systematics and evolution of ticks with a list of valid genus and species names. Parasitology. 2004;Suppl. 129:S15–S36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

