Prophylactic DNA vaccine targeting Foxp3+ regulatory T cells depletes myeloid-derived suppressor cells and improves anti-melanoma immune responses in a murine model
- PMID: 29124314
- PMCID: PMC11028379
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-017-2088-6
Prophylactic DNA vaccine targeting Foxp3+ regulatory T cells depletes myeloid-derived suppressor cells and improves anti-melanoma immune responses in a murine model
Abstract
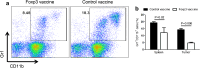
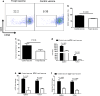
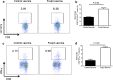
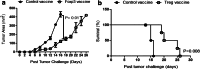
Regulatory T cells (Treg) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) are the two important and interactive immunosuppressive components of the tumor microenvironment that hamper anti-tumor immune responses. Therefore, targeting these two populations together might be beneficial for overcoming immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. We have recently shown that prophylactic Foxp3 DNA/recombinant protein vaccine (Foxp3 vaccine) promotes immunity against Treg in tumor-free conditions. In the present study, we investigated the immune modulatory effects of a prophylactic regimen of the redesigned Foxp3 vaccine in the B16F10 melanoma model. Our results indicate that Foxp3 vaccination continuously reduces Treg population in both the tumor site and the spleen. Surprisingly, Treg reduction was associated with a significant decrease in the frequency of MDSC, both in the spleen and in the tumor environment. Furthermore, Foxp3 vaccination resulted in a significant reduction of arginase-1(Arg-1)-induced nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), reactive oxygen species (ROS) and suppressed MDSC activity. Moreover, this concurrent depletion restored production of inflammatory cytokine IFN-γ and enhanced tumor-specific CTL response, which subsequently resulted in the reduction of tumor growth and the improved survival rate of vaccinated mice. In conclusion, our results revealed that Foxp3 vaccine promotes an immune response against tumor by targeting both Treg and MDSC, which could be exploited as a potential immunotherapy approach.
Keywords: Foxp3; Melanoma; Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; Regulatory T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-regulatory T cell vaccines in immunotherapy: focusing on FoxP3 as target.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(3):620-624. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1545625. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30633616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved Anti-Treg Vaccination Targeting Foxp3 Efficiently Decreases Regulatory T Cells in Mice.J Immunother. 2016 Sep;39(7):269-75. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000133. J Immunother. 2016. PMID: 27404943
-
Novel and enhanced anti-melanoma DNA vaccine targeting the tyrosinase protein inhibits myeloid-derived suppressor cells and tumor growth in a syngeneic prophylactic and therapeutic murine model.Cancer Gene Ther. 2014 Dec;21(12):507-17. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2014.56. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 25394503
-
Generation of multiepitope cancer vaccines based on large combinatorial libraries of survivin-derived mutant epitopes.Immunology. 2020 Oct;161(2):123-138. doi: 10.1111/imm.13233. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 32619293 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Trypanosoma cruzi Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Aug 27;11:737364. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.737364. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34513737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HER2 amplification subtype intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma exhibits high mutation burden and T cell exhaustion microenvironment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Aug 28;150(8):403. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05894-0. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39198311 Free PMC article.
-
Photodynamic Therapy and Adaptive Immunity Induced by Reactive Oxygen Species: Recent Reports.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 28;16(5):967. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050967. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenous interleukin-33 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth by remodelling the tumour microenvironment.J Transl Med. 2020 Dec 11;18(1):477. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02661-w. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33308251 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-regulatory T cell vaccines in immunotherapy: focusing on FoxP3 as target.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(3):620-624. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1545625. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30633616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of PD-1 Blockade in Cancer Immunotherapy.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 May 23;17:661-674. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.03.006. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31205619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995;155(3):1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Wolf AM, Wolf D, Steurer M, Gastl G, Gunsilius E, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. Increase of regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(2):606–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

