Mesoporous carbon nanomaterials in drug delivery and biomedical application
- PMID: 29124979
- PMCID: PMC8812584
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1399300
Mesoporous carbon nanomaterials in drug delivery and biomedical application
Abstract
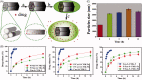
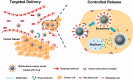
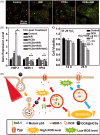
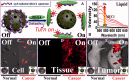
Recent development of nano-technology provides highly efficient and versatile treatment methods to achieve better therapeutic efficacy and lower side effects of malignant cancer. The exploration of drug delivery systems (DDSs) based on nano-material shows great promise in translating nano-technology to clinical use to benefit patients. As an emerging inorganic nanomaterial, mesoporous carbon nanomaterials (MCNs) possess both the mesoporous structure and the carbonaceous composition, endowing them with superior nature compared with mesoporous silica nanomaterials and other carbon-based materials, such as carbon nanotube, graphene and fullerene. In this review, we highlighted the cutting-edge progress of carbon nanomaterials as drug delivery systems (DDSs), including immediate/sustained drug delivery systems and controlled/targeted drug delivery systems. In addition, several representative biomedical applications of mesoporous carbon such as (1) photo-chemo synergistic therapy; (2) delivery of therapeutic biomolecule and (3) in vivo bioimaging are discussed and integrated. Finally, potential challenges and outlook for future development of mesoporous carbon in biomedical fields have been discussed in detail.
Keywords: Mesoporous carbon nanomaterials; biocompatibility; biomedical applications; drug delivery systems; photothermal therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ai K, Liu Y, Ruan C, et al. (2013). Sp2 C-dominant N-doped carbon sub-micrometer spheres with a tunable size: a versatile platform for highly efficient oxygen-reduction catalysts. Adv Mater 25:998–1003. - PubMed
-
- Akhavan O, Ghaderi E. (2013). Graphene nanomesh promises extremely efficient in vivo photothermal therapy. Small 9:3593–601. - PubMed
-
- Alhmoud H, Delalat B, Elnathan R, et al. (2015). Porous silicon nanodiscs for targeted drug delivery. Adv Funct Mater 25:1137–45.
-
- Bai L, Zhao Q, Wang J, et al. (2015). Mechanism study on pH-responsive cyclodextrin capped mesoporous silica: effect of different stalk densities and the type of cyclodextrin. Nanotechnology 26:165704. - PubMed
-
- Boesch D, Gavériaux C, Jachez B, et al. (1991). In vivo circumvention of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance of tumor cells with SDZ PSC 833. Cancer Res 51:4226–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
