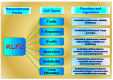
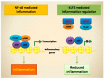
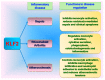
KLF2 in Regulation of NF-κB-Mediated Immune Cell Function and Inflammation
- PMID: 29125549
- PMCID: PMC5713352
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18112383
KLF2 in Regulation of NF-κB-Mediated Immune Cell Function and Inflammation
Abstract
KLF2 (Kruppel-like factor 2) is a member of the zinc finger transcription factor family, which critically regulates embryonic lung development, function of endothelial cells and maintenance of quiescence in T-cells and monocytes. It is expressed in naïve T-cells and monocytes, however its level of expression decreases during activation and differentiation. KLF2 also plays critical regulatory role in various inflammatory diseases and their pathogenesis. Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) is an important inducer of inflammation and the inflammation is mediated through the transcription of several proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules. So, both transcriptional factors KLF2 and NF-κB are being associated with the similar cellular functions and their maintenance. It was shown that KLF2 regulates most of the NF-κB-mediated activities. In this review, we focused on emphasizing the involvement of KLF2 in health and disease states and how they interact with transcriptional master regulator NF-κB.
Keywords: KLF2; NF-κB; immune cells; inflammation and diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) regulates proinflammatory activation of monocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Apr 25;103(17):6653-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508235103. Epub 2006 Apr 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16617118 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor KLF2 and Its Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Processes.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020 Jan;85(1):54-67. doi: 10.1134/S0006297920010058. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020. PMID: 32079517 Review.
-
Transcription factor MEF2C suppresses endothelial cell inflammation via regulation of NF-κB and KLF2.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Jun;230(6):1310-20. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24870. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25474999 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm-Conditioned Medium Impairs Macrophage-Mediated Antibiofilm Immune Response by Upregulating KLF2 Expression.Infect Immun. 2019 Mar 25;87(4):e00643-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00643-18. Print 2019 Apr. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 30692179 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Krüppel-like factor-2 in kidney disease.Nephrology (Carlton). 2018 Oct;23 Suppl 4:53-56. doi: 10.1111/nep.13456. Nephrology (Carlton). 2018. PMID: 30298668 Review.
Cited by
-
miR‑155 promotes an inflammatory response in HaCaT cells via the IRF2BP2/KLF2/NF‑κB pathway in psoriasis.Int J Mol Med. 2024 Nov;54(5):91. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5415. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39219281 Free PMC article.
-
siRNA-Mediated Timp1 Silencing Inhibited the Inflammatory Phenotype during Acute Lung Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 13;24(2):1641. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021641. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675165 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin combined with dexamethasone promote hematoma absorption in an optimized rat model of chronic subdural hematoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Nov 23;13(22):24815-24828. doi: 10.18632/aging.203717. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34813498 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Profiling of Atlantic Salmon Adherent Head Kidney Leukocytes Reveals That Macrophages Are Selectively Enriched During Culture.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 16;12:709910. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.709910. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484211 Free PMC article.
-
Potential therapeutic effects of interleukin-35 on the differentiation of naïve T cells into Helios+Foxp3+ Tregs in clinical and experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome.Mol Immunol. 2021 Apr;132:236-249. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.01.009. Epub 2021 Jan 16. Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33494935 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources