Rapid Determination of Major Compounds in the Ethanol Extract of Geopropolis from Malaysian Stingless Bees, Heterotrigona itama, by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS and NMR
- PMID: 29125569
- PMCID: PMC6150372
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22111935
Rapid Determination of Major Compounds in the Ethanol Extract of Geopropolis from Malaysian Stingless Bees, Heterotrigona itama, by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS and NMR
Abstract
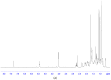
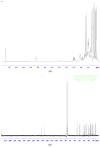
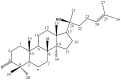
A reliable, rapid analytical method was established for the characterization of constituents of the ethanol extract of geopropolis (EEGP) produced by Malaysian stingless bees-Heterotrigona itama-by combining ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS). Based on known standards, the online METLIN database, and published literature, 28 compounds were confirmed. Phenolic acids, flavones, triterpenes and phytosterol were identified or tentatively identified using characteristic diagnostic fragment ions. The results indicated that terpenoids were the main components of EEGP, accompanied by low levels of phenolic acids, flavonoids, and phytosterol. Two major components were further purified by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography (PHPLC) and identified by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) as 24(E)-cycloart-24-ene-26-ol-3-one and 20-hydroxy-24-dammaren-3-one. These two triterpenes, confirmed in this geopropolis for the first time, are potential chemical markers for the identification of geopropolis from Malaysian stingless bees, H. itama.
Keywords: Heterotrigona itama; UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS; geopropolis; stingless bees.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Optimized extraction based on the terpenoids of Heterotrigona itama propolis and their antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities.J Food Biochem. 2020 Aug;44(8):e13296. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13296. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Food Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32529646
-
Metabolomics analysis of (Geo)propolis from Brazilian stingless bees by FIA and UHPLC-HRMS (Orbitrap).J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2025 Jan 1;252:116497. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116497. Epub 2024 Oct 5. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2025. PMID: 39383540
-
Characterisation of phenolic compounds by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS of geopropolis from the stingless bee Melipona subnitida (jandaíra).Phytochem Anal. 2018 Nov;29(6):549-558. doi: 10.1002/pca.2766. Epub 2018 May 17. Phytochem Anal. 2018. PMID: 29770982
-
Propolis and geopropolis from stingless bees as a source of bioactive compounds with antioxidant and antimicrobial action: A review.Food Res Int. 2025 Aug;214:116674. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116674. Epub 2025 May 19. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40467271 Review.
-
Use of Stingless Bee Propolis and Geopropolis against Cancer-A Literature Review of Preclinical Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Nov 14;14(11):1161. doi: 10.3390/ph14111161. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic, and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities of Ethanol Extract and Chemical Constituents Isolated from Homotrigona apicalis Propolis-In Vitro and Molecular Docking Studies.Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;13(8):1682. doi: 10.3390/life13081682. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629539 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study for Nutritional and Phytochemical Profiling of Coffea arabica (C. arabica) from Different Origins and Their Antioxidant Potential and Molecular Docking.Molecules. 2022 Aug 11;27(16):5126. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165126. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014363 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from Exploring Chemical Space and Chemical Diversity of Propolis Components.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 15;21(14):4988. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144988. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32679731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Untargeted Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS) Metabolomics Reveals Propolis Markers of Greek and Chinese Origin.Molecules. 2021 Jan 16;26(2):456. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020456. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33467182 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS Characterization of Phenolic Metabolites and Their Antioxidant Activities from Australian Native Plants.Metabolites. 2022 Oct 24;12(11):1016. doi: 10.3390/metabo12111016. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36355099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dutra R.P., Nogueira A.M.C., de Oliveira Marques R.R., Costa M.C.P., Ribeiro M.N.S. Avaliação farmacognóstica de geoprópolis de Melipona fasciculata Smith da Baixada maranhense, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2008;18:557–562. doi: 10.1590/S0102-695X2008000400010. - DOI
-
- Dutra R.P., Abreu B.V., Cunha M.S., Batista M.C., Torres L.M., Nascimento F.R., Ribeiro M.N., Guerra R.N. Phenolic acids, hydrolyzable tannins, and antioxidant activity of geopropolis from the stingless bee Melipona fasciculata Smith. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014;62:2549–2557. doi: 10.1021/jf404875v. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Quezada-Euán J.J.G., de Jesús May-Itzá W., González-Acereto J.A. Meliponiculture in Mexico: Problems and perspective for development. Bee World. 2001;82:160–167. doi: 10.1080/0005772X.2001.11099523. - DOI
-
- Liberio S.A., Pereira A.L., Dutra R.P., Reis A.S., Araujo M.J., Mattar N.S., Silva L.A., Ribeiro M.N., Nascimento F.R., Guerra R.N., et al. Antimicrobial activity against oral pathogens and immunomodulatory effects and toxicity of geopropolis produced by the stingless bee Melipona fasciculata Smith. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011;11 doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

