Silybin, a Major Bioactive Component of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaernt.)-Chemistry, Bioavailability, and Metabolism
- PMID: 29125572
- PMCID: PMC6150307
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22111942
Silybin, a Major Bioactive Component of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaernt.)-Chemistry, Bioavailability, and Metabolism
Abstract
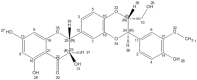
Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) is a medicinal plant that has been used for thousands of years as a remedy for a variety of ailments. The main component of S. marianum fruit extract (silymarin) is a flavonolignan called silybin, which is not only the major silymarin element but is also the most active ingredient of this extract, which has been confirmed in various studies. This compound belongs to the flavonoid group known as flavonolignans. Silybin's structure consists in two main units. The first is based on a taxifolin, the second a phenyllpropanoid unit, which in this case is conyferil alcohol. These two units are linked together into one structure by an oxeran ring. Since the 1970s, silybin has been regarded in official medicine as a substance with hepatoprotective properties. There is a large body of research that demonstrates silybin's many other healthy properties, but there are still a lack of papers focused on its molecular structure, chemistry, metabolism, and novel form of administration. Therefore, the aim of this paper is a literature review presenting and systematizing our knowledge of the silybin molecule, with particular emphasis on its structure, chemistry, bioavailability, and metabolism.
Keywords: bioavailability; chemistry; silybin; silymarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rainone F. Milk thistle. Am. Fam. Physician. 2005;72:1285–1288. - PubMed
-
- Szilard S., Szentgyorgyi D., Demeter I. Protective effect of Legalon in workers exposed to organic solvents. Acta Med. Hung. 1988;45:249–256. - PubMed
-
- Feher J., Deak G., Muzes G., Lang I., Niederland V., Nekam K., Karteszi M. Liver-protective action of silymarin therapy in chronic alcoholic liver diseases. Orv. Hetil. 1989;130:2723–2727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources