Imaging PD-L1 Expression with ImmunoPET
- PMID: 29125731
- PMCID: PMC5773933
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00631
Imaging PD-L1 Expression with ImmunoPET
Abstract
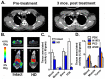
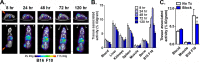
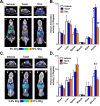
High sensitivity imaging tools could provide a more holistic view of target antigen expression to improve the identification of patients who might benefit from cancer immunotherapy. We developed for immunoPET a novel recombinant human IgG1 (termed C4) that potently binds an extracellular epitope on human and mouse PD-L1 and radiolabeled the antibody with zirconium-89. Small animal PET/CT studies showed that 89Zr-C4 detected antigen levels on a patient derived xenograft (PDX) established from a non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient before an 8-month response to anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA4 therapy. Importantly, the concentration of antigen is beneath the detection limit of previously developed anti-PD-L1 radiotracers, including radiolabeled atezolizumab. We also show that 89Zr-C4 can specifically detect antigen in human NSCLC and prostate cancer models endogenously expressing a broad range of PD-L1. 89Zr-C4 detects mouse PD-L1 expression changes in immunocompetent mice, suggesting that endogenous PD-1/2 will not confound human imaging. Lastly, we found that 89Zr-C4 could detect acute changes in tumor expression of PD-L1 due to standard of care chemotherapies. In summary, we present evidence that low levels of PD-L1 in clinically relevant cancer models can be imaged with immunoPET using a novel recombinant human antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Michael J. Evans received consulting fees and owns shares in ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Michael J. Evans received research support from GE Healthcare.
Figures

References
-
- Carbognin L.; Pilotto S.; Milella M.; Vaccaro V.; Brunelli M.; Calio A.; Cuppone F.; Sperduti I.; Giannarelli D.; Chilosi; et al. (2015) Differential Activity of Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab and MPDL3280A according to the Tumor Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand-1 (PD-L1): Sensitivity Analysis of Trials in Melanoma, Lung and Genitourinary Cancers. PLoS One 10, e0130142.10.1371/journal.pone.0130142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herbst R. S.; Soria J. C.; Kowanetz M.; Fine G. D.; Hamid O.; Gordon M. S.; Sosman J. A.; McDermott D. F.; Powderly J. D.; Gettinger S. N.; et al. (2014) Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 515, 563–7. 10.1038/nature14011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

