Synaptic plasticity may underlie l-DOPA induced dyskinesia
- PMID: 29125979
- PMCID: PMC5825254
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2017.10.021
Synaptic plasticity may underlie l-DOPA induced dyskinesia
Abstract
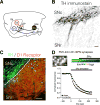
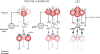
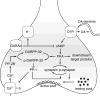
l-DOPA provides highly effective treatment for Parkinson's disease, but l-DOPA induced dyskinesia (LID) is a very debilitating response that eventually is presented by a majority of patients. A central issue in understanding the basis of LID is whether it is due to a response to chronic l-DOPA over years of therapy, and/or due to synaptic changes that follow the loss of dopaminergic neurotransmission and then triggered by acute l-DOPA administration. We review recent work that suggests that specific synaptic changes in the D1 dopamine receptor-expressing direct pathway striatal projection neurons due to loss of dopamine in Parkinson's disease are responsible for LID. Chronic l-DOPA may nevertheless modulate LID through priming mechanisms.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors disclose no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aquino CC, Fox SH. Clinical spectrum of levodopa-induced complications. Mov Disord. 2015;30:80–89. - PubMed
-
- Bastide MF, Meissner WG, Picconi B, Fasano S, Fernagut PO, Feyder M, Francardo V, Alcacer C, Ding Y, Brambilla R, et al. Pathophysiology of L-dopa-induced motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2015;132:96–168. - PubMed
-
- Jenner P. Molecular mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:665–677. - PubMed
-
- Iravani MM, McCreary AC, Jenner P. Striatal plasticity in Parkinson’s disease and L-dopa induced dyskinesia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012;18(Suppl 1):S123–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

