α-Lipoic acid improves abnormal behavior by mitigation of oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis, and tauopathy in P301S Tau transgenic mice
- PMID: 29126071
- PMCID: PMC5684493
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.001
α-Lipoic acid improves abnormal behavior by mitigation of oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis, and tauopathy in P301S Tau transgenic mice
Abstract
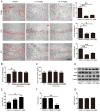
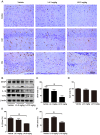
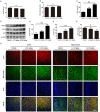
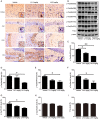
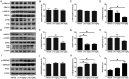
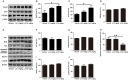
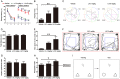
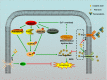
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease and is characterized by neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) composed of Tau protein. α-Lipoic acid (LA) has been found to stabilize the cognitive function of AD patients, and animal study findings have confirmed its anti-amyloidogenic properties. However, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear, especially with respect to the ability of LA to control Tau pathology and neuronal damage. Here, we found that LA supplementation effectively inhibited the hyperphosphorylation of Tau at several AD-related sites, accompanied by reduced cognitive decline in P301S Tau transgenic mice. Furthermore, we found that LA not only inhibited the activity of calpain1, which has been associated with tauopathy development and neurodegeneration via modulating the activity of several kinases, but also significantly decreased the calcium content of brain tissue in LA-treated mice. Next, we screened for various modes of neural cell death in the brain tissue of LA-treated mice. We found that caspase-dependent apoptosis was potently inhibited, whereas autophagy did not show significant changes after LA supplementation. Interestingly, Tau-induced iron overload, lipid peroxidation, and inflammation, which are involved in ferroptosis, were significantly blocked by LA administration. These results provide compelling evidence that LA plays a role in inhibiting Tau hyperphosphorylation and neuronal loss, including ferroptosis, through several pathways, suggesting that LA may be a potential therapy for tauopathies.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Ferroptosis; Oxidative stress; Tau; α-Lipoic acid.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Organotypic brain slice cultures of adult transgenic P301S mice--a model for tauopathy studies.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45017. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045017. Epub 2012 Sep 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984603 Free PMC article.
-
A novel transgenic mouse expressing double mutant tau driven by its natural promoter exhibits tauopathy characteristics.Exp Neurol. 2008 Jul;212(1):71-84. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.03.007. Epub 2008 Mar 21. Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18490011
-
Locus Coeruleus Ablation Exacerbates Cognitive Deficits, Neuropathology, and Lethality in P301S Tau Transgenic Mice.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 3;38(1):74-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1483-17.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 13. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29133432 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of murine tau gene increases tau aggregation in a human mutant tau transgenic mouse model.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):1001-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0381001. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20658993 Review.
-
Current advances on different kinases involved in tau phosphorylation, and implications in Alzheimer's disease and tauopathies.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2005 Jan;2(1):3-18. doi: 10.2174/1567205052772713. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2005. PMID: 15977985 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of narcotics on ferroptosis-related molecular mechanisms and signalling pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1020447. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1020447. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36313359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of ferroptosis pathways in neuroinflammation and neurological disorders: From pathogenesis to treatment.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 19;10(3):e24786. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24786. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38314277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into the potential role of ferroptosis in neurodegenerative diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Oct 27;16:1005182. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1005182. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36385946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron dyshomeostasis and ferroptosis in Alzheimer's disease: Molecular mechanisms of cell death and novel therapeutic drugs and targets for AD.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 16;13:983623. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.983623. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nurr1 Promotes Lung Cancer Apoptosis Via Enhancing Mitochondrial Stress and p53-Drp1 Pathway.Open Life Sci. 2019 Jul 10;14:262-274. doi: 10.1515/biol-2019-0030. eCollection 2019 Jan. Open Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 33817160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoshiyama Y., Higuchi M., Zhang B., Huang S.M., Iwata N., Saido T.C., Maeda J., Suhara T., Trojanowski J.Q., Lee V.M. Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron. 2007;53(3):337–351. - PubMed
-
- Lee V.M., Goedert M., Trojanowski J.Q. Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;24:1121–1159. - PubMed
-
- DeVos S.L., Miller R.L., Schoch K.M., Holmes B.B., Kebodeaux C.S., Wegener A.J., Chen G., Shen T., Tran H., Nichols B., Zanardi T.A., Kordasiewicz H.B., Swayze E.E., Bennett C.F., Diamond M.I., Miller T.M. Tau reduction prevents neuronal loss and reverses pathological tau deposition and seeding in mice with tauopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017;9(374) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holtzman D.M., Carrillo M.C., Hendrix J.A., Bain L.J., Catafau A.M., Gault L.M., Goedert M., Mandelkow E., Mandelkow E.M., Miller D.S., Ostrowitzki S., Polydoro M., Smith S., Wittmann M., Hutton M. Tau: from research to clinical development. Alzheimer's & dementia. J. Alzheimer's Assoc. 2016;12(10):1033–1039. - PubMed
-
- Perez M., Cuadros R., Smith M.A., Perry G., Avila J. Phosphorylated, but not native, tau protein assembles following reaction with the lipid peroxidation product, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. FEBS Lett. 2000;486(3):270–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

