MiRNA-513a-5p inhibits progesterone receptor expression and constitutes a risk factor for breast cancer: the hOrmone and Diet in the ETiology of breast cancer prospective study
- PMID: 29126102
- PMCID: PMC6454510
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgx126
MiRNA-513a-5p inhibits progesterone receptor expression and constitutes a risk factor for breast cancer: the hOrmone and Diet in the ETiology of breast cancer prospective study
Abstract
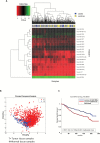
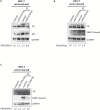
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) might be considered both predictors and players of cancer development. The aim of the present report was to investigate whether many years before the diagnosis of breast cancer miRNA expression is already disregulated. In order to test this hypothesis, we compared miRNAs extracted from leukocytes in healthy women who later developed breast cancer and in women who remain healthy during the whole 15-year follow-up time. Accordantly, we used a case-control study design nested in the hOrmone and Diet in the ETiology of breast cancer (ORDET) prospective cohort study addressing the possibility that miRNAs can serve as both early biomarkers and components of the hormonal etiological pathways leading to breast cancer development in premenopausal women. We compared leukocyte miRNA profiles of 191 incident premenopausal breast cancer cases and profiles of 191 women who remained healthy over a follow-up period of 20 years. The analysis identified 20 differentially expressed miRNAs in women candidate to develop breast cancer versus control women. The upregulated miRNAs, miR-513-a-5p, miR-513b-5p and miR-513c-5p were among the most significantly deregulated miRNAs. In multivariate analysis, miR-513a-5p upregulation was directly and statistically significant associated with breast cancer risk (OR = 1.69; 95% CI 1.08-2.64; P = 0.0293). In addition, the upregulation of miR-513-a-5p displayed the strongest direct association with serum progesterone and testosterone levels. The experimental data corroborated the inhibitory function of miR-513a-5p on progesterone receptor expression confirming that progesterone receptor is a target of miR-513a-5p. The identification of upregulated miR-513a-5p with its oncogenic potential further validates the use of miRNAs as long-term biomarker of breast cancer risk.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of microRNA biomarkers in the blood of breast cancer patients based on microRNA profiling.Gene. 2017 Jul 1;619:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.03.038. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28359916
-
Plasma Circulating Mirnas Profiling for Identification of Potential Breast Cancer Early Detection Biomarkers.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 May 1;22(5):1375-1381. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.5.1375. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34048164 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of microRNAs 145-3p and 145-5p is a long-term predictor of postmenopausal breast cancer risk: The ORDET prospective study.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 Nov;23(11):2471-81. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0398. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014. PMID: 25073626
-
A two-miRNA signature of upregulated miR-185-5p and miR-362-5p as a blood biomarker for breast cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Jun;222:153458. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153458. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33962174
-
Prospectives of mirna gene signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154658. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154658. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37421840 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-513c-5p is involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia by regulating of low-density lipoprotein receptor-associated protein 6.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021 Dec 20;21(1):837. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-04069-w. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021. PMID: 34930169 Free PMC article.
-
LINC01436 Promotes the Progression of Gastric Cancer via Regulating miR-513a-5p/APE1 Axis.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 19;13:10607-10619. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S257747. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. Retraction in: Onco Targets Ther. 2022 Jun 23;15:701-702. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S379383. PMID: 33116638 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
miR-513c-5p Suppression Aggravates Pyroptosis of Endothelial Cell in Deep Venous Thrombosis by Promoting Caspase-1.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 4;10:838785. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.838785. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35445025 Free PMC article.
-
Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA LINC00922 Aggravates the Malignant Phenotype of Breast Cancer by Regulating the microRNA-424-5p/BDNF Axis.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Aug 21;12:7539-7552. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S267665. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. Retraction in: Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Oct 04;13:7595-7596. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S341930. PMID: 32904382 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
High dose androgen suppresses natural killer cytotoxicity of castration-resistant prostate cancer cells via altering AR/circFKBP5/miRNA-513a-5p/PD-L1 signals.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Aug 29;13(8):746. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04956-w. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36038573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fletcher C.E., et al. (2014)Interplay between steroid signalling and microRNAs: implications for hormone-dependent cancers. Endocr. Relat. Cancer, 21, R409–R429. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W., et al. (2008)Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight?Nat. Rev. Genet., 9, 102–114. - PubMed
-
- Acunzo M., et al. (2015)MicroRNA and cancer–a brief overview. Adv. Biol. Regul., 57, 1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

