High-density lipoprotein cholesterol efflux capacity is inversely associated with cardiovascular risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29126414
- PMCID: PMC5681808
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0604-5
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol efflux capacity is inversely associated with cardiovascular risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: A low plasma level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (HDL-C) is associated with cardiovascular risk. A key cardioprotective property of HDL is cholesterol efflux capacity (CEC), the ability of HDL to accept cholesterol from macrophages. In this study, we aimed to identify the predictive value of CEC for cardiovascular risk.
Methods: The relative risks (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were pooled to analyze the association between CEC and the incidence of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality. The odds ratios (ORs) and 95% CIs were pooled to estimate the association of CEC and the prevalence of cardiovascular events.
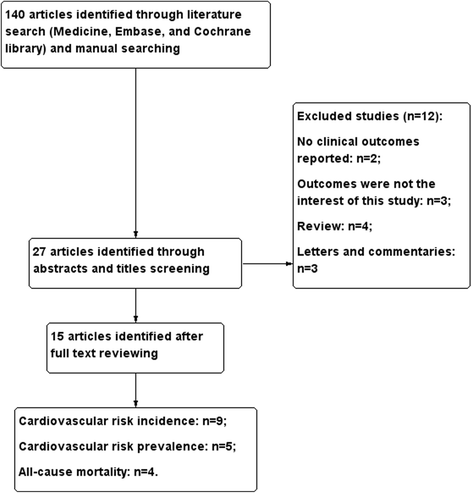
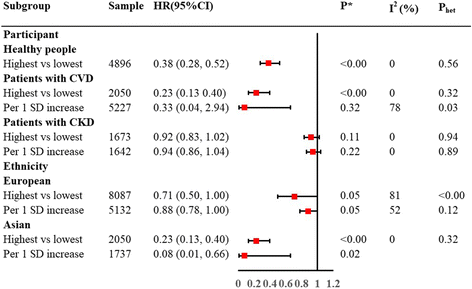
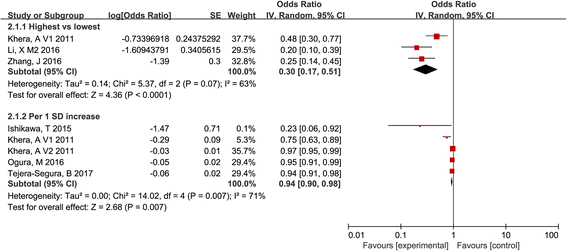
Results: A total of 15 studies were included. Results showed that the highest CEC was significantly associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular events incidents compared to the lowest CEC (RR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.85; I 2, 89%); the pooled RR of cardiovascular risk for per unit SD increase was 0.87 (95% CI, 0.73 to 1.04; I 2, 67%). Dose-response curve indicated that cardiovascular risk decreased by 39% (RR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.51 to 0.74) for per unit CEC increase. Similarly, an inverse association was observed between CEC and the prevalence of cardiovascular events (highest vs. lowest, OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.17 to 0.5; I 2 = 63%; per unit SD increase, OR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.90 to 0.98; I 2 = 71%). However, based on the current data, CEC was not significantly associated with all-cause mortality.
Conclusions: Findings from this meta-analysis suggest that HDL-mediated CEC is inversely associated with cardiovascular risk, which appears to be independent of HDL concentration. The growing understanding of CEC and its role in cardiovascular risk decrease may improve the accuracy of cardiovascular risk prediction and also open important avenues to develop novel therapeutic targeting HDL metabolism.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk; Cholesterol efflux capacity; High-density lipoprotein; Meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey MC, Blum CB, Eckel RH, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129(25 Suppl 2):S1–45. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000437738.63853.7a. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

