Framing the conversation: use of PRECIS-2 ratings to advance understanding of pragmatic trial design domains
- PMID: 29126437
- PMCID: PMC5681765
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2267-y
Framing the conversation: use of PRECIS-2 ratings to advance understanding of pragmatic trial design domains
Abstract
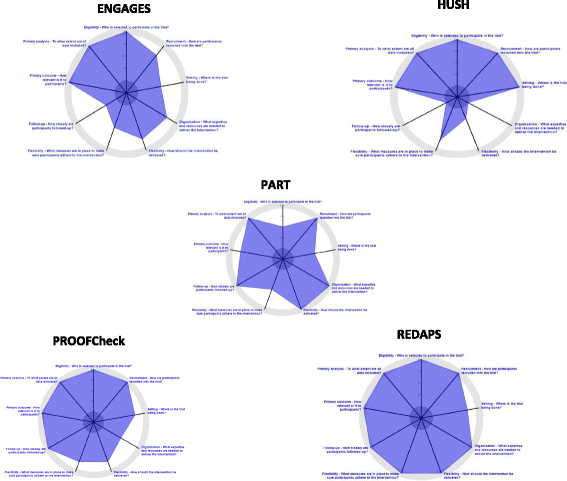
Background: There continues to be debate about what constitutes a pragmatic trial and how it is distinguished from more traditional explanatory trials. The NIH Pragmatic Trials Collaborative Project, which includes five trials and a coordinating unit, has adopted the Pragmatic-Explanatory Continuum Indicator Summary (PRECIS-2) instrument. The purpose of the study was to collect PRECIS-2 ratings at two points in time to assess whether the tool was sensitive to change in trial design, and to explore with investigators the rationale for rating shifts.
Methods: A mixed-methods design included sequential collection and analysis of quantitative data (PRECIS-2 ratings) and qualitative data. Ratings were collected at two annual, in-person project meetings, and subsequent interviews conducted with investigators were recorded, transcribed, and coded using NVivo 11 Pro for Windows. Rating shifts were coded as either (1) actual change (reflects a change in procedure or protocol), (2) primarily a rating shift reflecting rater variability, or (3) themes that reflect important concepts about the tool and/or pragmatic trial design.
Results: Based on PRECIS-2 ratings, each trial was highly pragmatic at the planning phase and remained so 1 year later in the early phases of trial implementation. Over half of the 45 paired ratings for the nine PRECIS-2 domains indicated a rating change from Time 1 to Time 2 (N = 24, 53%). Of the 24 rating changes, only three represented a true change in the design of the trial. Analysis of rationales for rating shifts identified critical themes associated with the tool or pragmatic trial design more generally. Each trial contributed one or more relevant comments, with Eligibility, Flexibility of Adherence, and Follow-up each accounting for more than one.
Conclusions: PRECIS-2 has proved useful for "framing the conversation" about trial design among members of the Pragmatic Trials Collaborative Project. Our findings suggest that design elements assessed by the PRECIS-2 tool may represent mostly stable decisions. Overall, there has been a positive response to using PRECIS-2 to guide conversations around trial design, and the project's focus on the use of the tool by this group of early adopters has provided valuable feedback to inform future trainings on the tool.
Keywords: Effectiveness trials; Mixed methods; PRECIS-2 tool; Pragmatic trials; Trial design.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Westat IRB reviews all studies involving research on human subjects. Exemption from IRB review was received from the Chair of the Westat Institutional Review Board (IRB) on 23 October 2014 (FWA 00005551). According to [45 CFR 46.101(b5)] and a letter received on 16 October 2014, from Denise Bonds, Medical Officer, NHLBI; this research involves a program evaluation and, therefore, is exempt from IRB review.
Westat is conducting an evaluation of the methods and processes that contribute to successful, pragmatic, low-cost clinical trials. The work involves monitoring the design/planning of these trials and, in years 2–5, the implementation of the trials. As members of this cooperative agreement, all investigators consented to participate in these activities and, specifically, provided oral consent prior to the conduct of the interviews as reported in this submission.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A dynamic application of PRECIS-2 to evaluate implementation in a pragmatic, cluster randomized clinical trial in two nursing home systems.Trials. 2018 Aug 22;19(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2817-y. Trials. 2018. PMID: 30134976 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Use of PRECIS ratings in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Health Care Systems Research Collaboratory.Trials. 2016 Jan 16;17:32. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1158-y. Trials. 2016. PMID: 26772801 Free PMC article.
-
Comments, suggestions, and criticisms of the Pragmatic Explanatory Continuum Indicator Summary-2 design tool: a citation analysis.J Clin Epidemiol. 2024 Dec;176:111534. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2024.111534. Epub 2024 Sep 14. J Clin Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 39284517
-
Trends in the Explanatory or Pragmatic Nature of Cardiovascular Clinical Trials Over 2 Decades.JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Nov 1;4(11):1122-1128. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.3604. JAMA Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31473763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are trials of psychological and psychosocial interventions for schizophrenia and psychosis included in the NICE guidelines pragmatic? A systematic review.PLoS One. 2019 Sep 24;14(9):e0222891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222891. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31550279 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the effects of pycnogenol (French maritime pine bark extract) supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers and nutritional and clinical status in traumatic brain injury patients in an intensive care unit: A randomized clinical trial protocol.Trials. 2020 Feb 11;21(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-4008-x. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32046747 Free PMC article.
-
A Call for Electronic Health Record-based Data Sharing for Clinical Trials in Critical Care.J Med Syst. 2018 May 25;42(7):115. doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-0984-8. J Med Syst. 2018. PMID: 29802451 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Physiotherapists as first-contact practitioners for patients with low back pain in French primary care: a pragmatic cluster randomised controlled trial.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Nov 18;24(1):1427. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11814-2. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39558330 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Using PRECIS-2 in Chinese herbal medicine randomized controlled trials for irritable bowel syndrome: A methodological exploration based on literature.Integr Med Res. 2024 Sep;13(3):101053. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2024.101053. Epub 2024 May 31. Integr Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39219983 Free PMC article.
-
Motivational Interviewing for Maternal Immunisation (MI4MI) study: a protocol for an implementation study of a clinician vaccine communication intervention for prenatal care settings.BMJ Open. 2020 Nov 17;10(11):e040226. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040226. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 33203635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rothwell PM. External validity of randomised controlled trials: “To whom do the results of this trial apply?”. Lancet. 2005;365(9453):82–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources