Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 is associated with shelterin complex at interstitial telomeric sites
- PMID: 29126443
- PMCID: PMC5681776
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-017-0160-2
Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 is associated with shelterin complex at interstitial telomeric sites
Abstract
Background: Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 (UCHL1) is primarily expressed in neuronal cells and neuroendocrine cells and has been associated with various diseases, including many cancers. It is a multifunctional protein involved in deubiquitination, ubiquitination and ubiquitin homeostasis, but its specific roles are disputed and still generally undetermined.
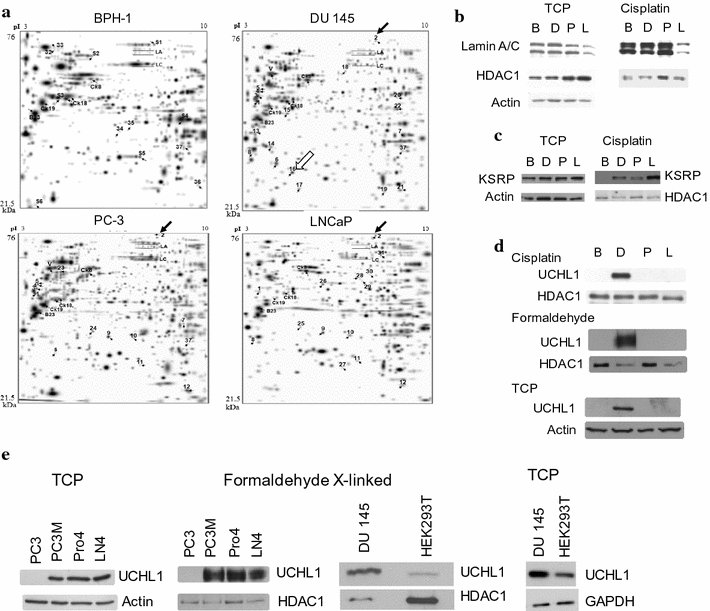
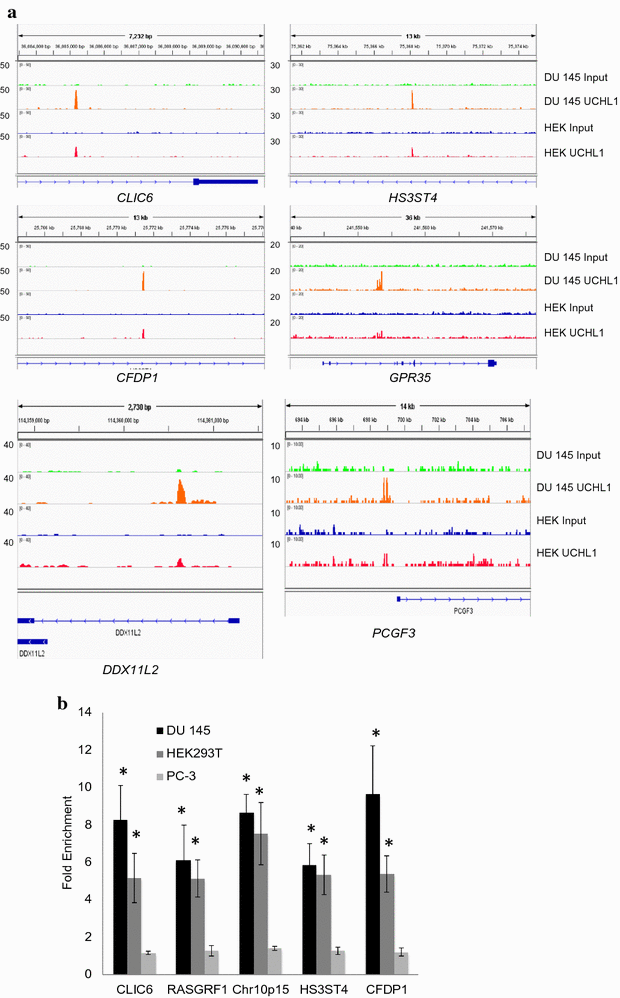
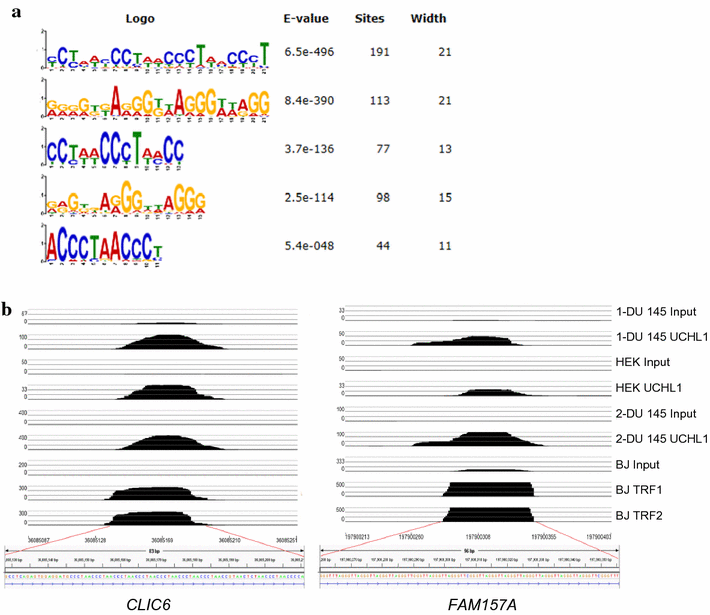
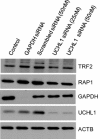
Results: Herein, we demonstrate that UCHL1 is associated with genomic DNA in certain prostate cancer cell lines, including DU 145 cells derived from a brain metastatic site, and in HEK293T embryonic kidney cells with a neuronal lineage. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and sequencing revealed that UCHL1 localizes to TTAGGG repeats at telomeres and interstitial telomeric sequences, as do TRF1 and TRF2, components of the shelterin complex. A weak or transient interaction between UCHL1 and the shelterin complex was confirmed by immunoprecipitation and proximity ligation assays. UCHL1 and RAP1, also known as TERF2IP and a component of the shelterin complex, were bound to the nuclear scaffold.
Conclusions: We demonstrated a novel feature of UCHL1 in binding telomeres and interstitial telomeric sites.
Keywords: Interstitial telomeric sites; Prostate cancer; Shelterin complex; UCHL1.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of in vivo TRF1 binding to chromatin restricts its location exclusively to telomeric repeats.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(23):3742-9. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.965044. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25483083 Free PMC article.
-
Human telomeric proteins occupy selective interstitial sites.Cell Res. 2011 Jul;21(7):1013-27. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.39. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21423278 Free PMC article.
-
TRF1 and TRF2 binding to telomeres is modulated by nucleosomal organization.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 13;43(12):5824-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv507. Epub 2015 May 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25999344 Free PMC article.
-
Shelterin: the protein complex that shapes and safeguards human telomeres.Genes Dev. 2005 Sep 15;19(18):2100-10. doi: 10.1101/gad.1346005. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 16166375 Review.
-
Post-translational modifications of TRF1 and TRF2 and their roles in telomere maintenance.Mech Ageing Dev. 2012 Jun;133(6):421-34. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2012.05.002. Epub 2012 May 23. Mech Ageing Dev. 2012. PMID: 22634377 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA-methylation and genomic copy number in primary tumors and corresponding lymph node metastases in prostate cancer from patients with low and high Gleason score.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023 Jan 21;39:100586. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100586. eCollection 2023 Mar. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36935856 Free PMC article.
-
UCH-L1 bypasses mTOR to promote protein biosynthesis and is required for MYC-driven lymphomagenesis in mice.Blood. 2018 Dec 13;132(24):2564-2574. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-848515. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30257881 Free PMC article.
-
At the Beginning of the End and in the Middle of the Beginning: Structure and Maintenance of Telomeric DNA Repeats and Interstitial Telomeric Sequences.Genes (Basel). 2019 Feb 5;10(2):118. doi: 10.3390/genes10020118. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30764567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

