Orchestrating phospholipid biosynthesis: Phosphatidic acid conducts and Opi1p performs
- PMID: 29127205
- PMCID: PMC5682977
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.H117.809970
Orchestrating phospholipid biosynthesis: Phosphatidic acid conducts and Opi1p performs
Abstract
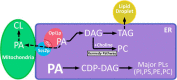
Phosphatidic acid (PA) and the conserved integral ER membrane protein Scs2p regulate localization of the transcriptional repressor Opi1p, which controls expression of phospholipid biosynthesis genes, but the mechanisms conducting Opi1p localization are not fully understood. A new study suggests the existence of a distinct pool of PA in the ER that is required for regulation of Opi1p localization and thus phospholipid metabolism in yeast.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Loewen C. J., Gaspar M. L., Jesch S. A., Delon C., Ktistakis N. T., Henry S. A., and Levine T. P. (2004) Phospholipid metabolism regulated by a transcription factor sensing phosphatidic acid. Science 304, 1644–1647 - PubMed
-
- Luévano-Martínez L. A., Appolinario P., Miyamoto S., Uribe-Carvajal S., and Kowaltowski A. J. (2013) Deletion of the transcriptional regulator opi1p decreases cardiolipin content and disrupts mitochondrial metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 60, 150–158 - PubMed
-
- Zhong Q., and Greenberg M. L. (2003) Regulation of phosphatidylglycerophosphate synthase by inositol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is not at the level of PGS1 mRNA abundance. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 33978–33984 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

