Reduced hepatitis B and D viral entry using clinically applied drugs as novel inhibitors of the bile acid transporter NTCP
- PMID: 29127322
- PMCID: PMC5681660
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15338-0
Reduced hepatitis B and D viral entry using clinically applied drugs as novel inhibitors of the bile acid transporter NTCP
Abstract
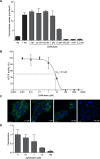
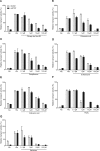
The sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP, SLC10A1) is the main hepatic transporter of conjugated bile acids, and the entry receptor for hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis delta virus (HDV). Myrcludex B, a synthetic peptide mimicking the NTCP-binding domain of HBV, effectively blocks HBV and HDV infection. In addition, Myrcludex B inhibits NTCP-mediated bile acid uptake, suggesting that also other NTCP inhibitors could potentially be a novel treatment of HBV/HDV infection. This study aims to identify clinically-applied compounds intervening with NTCP-mediated bile acid transport and HBV/HDV infection. 1280 FDA/EMA-approved drugs were screened to identify compounds that reduce uptake of taurocholic acid and lower Myrcludex B-binding in U2OS cells stably expressing human NTCP. HBV/HDV viral entry inhibition was studied in HepaRG cells. The four most potent inhibitors of human NTCP were rosiglitazone (IC50 5.1 µM), zafirlukast (IC50 6.5 µM), TRIAC (IC50 6.9 µM), and sulfasalazine (IC50 9.6 µM). Chicago sky blue 6B (IC50 7.1 µM) inhibited both NTCP and ASBT, a distinct though related bile acid transporter. Rosiglitazone, zafirlukast, TRIAC, sulfasalazine, and chicago sky blue 6B reduced HBV/HDV infection in HepaRG cells in a dose-dependent manner. Five out of 1280 clinically approved drugs were identified that inhibit NTCP-mediated bile acid uptake and HBV/HDV infection in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
Stephan Urban is co-applicant and co-inventor on patents protecting HBV preSderived lipopeptides (Myrcludex B) for the use of HBV/HDV entry inhibitors. The other authors who have taken part in this study declared that they do not have anything to disclose regarding funding or conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Viral entry of hepatitis B and D viruses and bile salts transportation share common molecular determinants on sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(6):3273-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03478-13. Epub 2014 Jan 3. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24390325 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclosporin A inhibits hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus entry by cyclophilin-independent interference with the NTCP receptor.J Hepatol. 2014 Apr;60(4):723-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.11.022. Epub 2013 Dec 1. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24295872
-
Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes.Gastroenterology. 2014 Apr;146(4):1070-83. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.12.024. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24361467
-
Molecular regulation of the hepatic bile acid uptake transporter and HBV entry receptor NTCP.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021 Aug;1866(8):158960. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158960. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33932583 Review.
-
Interactions of Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide with host cellular proteins upon hepatitis B and D virus infection: novel potential targets for antiviral therapy.Biol Chem. 2023 Apr 28;404(7):673-690. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2022-0345. Print 2023 Jun 27. Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37103224 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylation of Methyl 4-Hydroxy-2-thioxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate: Synthetic, Crystallographic, and Molecular Docking Studies.Molecules. 2020 Sep 16;25(18):4238. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184238. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32947763 Free PMC article.
-
ATP5B Is an Essential Factor for Hepatitis B Virus Entry.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 24;23(17):9570. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179570. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36076968 Free PMC article.
-
Troglitazone Impedes the Oligomerization of Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide and Entry of Hepatitis B Virus Into Hepatocytes.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 8;9:3257. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03257. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30671048 Free PMC article.
-
AI drug discovery screening for COVID-19 reveals zafirlukast as a repurposing candidate.Med Drug Discov. 2021 Mar;9:100077. doi: 10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100077. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Med Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 33521623 Free PMC article.
-
Selective hepatitis B and D virus entry inhibitors from the group of pentacyclic lupane-type betulin-derived triterpenoids.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 10;10(1):21772. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78618-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33303817 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

