The positive effects of Xueshuan Xinmai tablets on brain functional connectivity in acute ischemic stroke: a placebo controlled randomized trial
- PMID: 29127417
- PMCID: PMC5681502
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15456-9
The positive effects of Xueshuan Xinmai tablets on brain functional connectivity in acute ischemic stroke: a placebo controlled randomized trial
Abstract
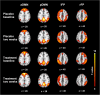
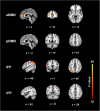
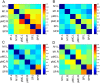
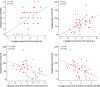
Through a placebo controlled randomized study, the purpose of this report was to investigate the effects of Xueshuan Xinmai tablets (XXMT) on neurologic deficits, quality of life and brain functional connectivity in acute ischemic stroke patients and to explore the mechanism of action of XXMT. In total, 44 acute ischemic stroke patients were randomly divided to the XXMT treatment group (n = 22) or the placebo group (n = 22) in a 2-week trial. Before and after the treatment, the neurological assessment and functional magnetic resonance imaging examinations were carried out. Compared to the placebo group, the scores of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) and Stroke-Specific Quality of Life Scale (SSQOL) significantly improved in the treatment group. In addition, XXMT-treated patients demonstrated significantly enhanced functional connectivity within the default mode, frontal-parietal, and motor control networks. Furthermore, the changed connectivity in the left precuneus was positively correlated to the improvement of NIHSS and SSQOL scores. The present study indicated that XXMT treatment significantly improved the neurologic deficit and quality of life of acute ischemic stroke patients and that the therapeutic effect may be based on the modulation of XXMT on the functional connectivity of brain networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Phan, K. et al. Endovascular therapy including thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Journal of clinical neuroscience: official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia, 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.12.025 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

