The effects of vitamin E or lipoic acid supplementation on oxyphytosterols in subjects with elevated oxidative stress: a randomized trial
- PMID: 29127425
- PMCID: PMC5681676
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15615-y
The effects of vitamin E or lipoic acid supplementation on oxyphytosterols in subjects with elevated oxidative stress: a randomized trial
Abstract
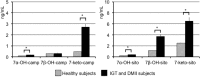
Despite increased serum plant sterol concentrations after consumption of plant sterol enriched margarines, plasma oxyphytosterol concentrations were not increased in healthy subjects. Here, we assessed plasma oxyphytosterol concentrations and whether they are affected by antioxidants in subjects with elevated oxidative stress. Twenty subjects with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) or type 2 diabetes (DM2) consumed for 4 weeks placebo, vitamin E (804 mg/d) or lipoic acid capsules (600 mg/d). Plasma and blood cell oxyphytosterol and oxycholesterol concentrations were determined in butylated hydroxytoluene-enriched EDTA plasma via GC-MS. Also, markers reflecting oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity were measured. Plasma oxycampesterol and oxysitosterol concentrations were 122% and 83% higher in IGT or DM2 subjects than in healthy subjects, as determined in an earlier study. Vitamin E or lipoic acid supplementation did not reduce plasma oxyphytosterol and oxycholesterol concentrations, or other markers reflecting oxidative stress or antioxidative capacity. Concentrations of different oxyphytosterols correlated within plasma, and within red blood cells and platelets. However, plasma and blood cell oxyphytosterol levels did not correlate. Although plasma oxyphytosterol concentrations are higher in IGT or DM2 subjects than in healthy subjects, 4-weeks vitamin E or lipoic acid supplementation does not lower plasma oxycholesterol or oxyphytosterol concentrations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxyphytosterol formation in humans: identification of high vs. low oxidizers.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Jul 1;86(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.02.035. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23500537 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of plant sterol- or stanol-enriched margarine on fasting plasma oxyphytosterol concentrations in healthy subjects.Atherosclerosis. 2013 Apr;227(2):414-9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.01.012. Epub 2013 Jan 21. Atherosclerosis. 2013. PMID: 23375753 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of plant stanol ester consumption on fasting plasma oxy(phyto)sterol concentrations as related to fecal microbiota characteristics.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 May;169:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.02.029. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 26940357 Clinical Trial.
-
Postprandial plasma oxyphytosterol concentrations after consumption of plant sterol or stanol enriched mixed meals in healthy subjects.Steroids. 2015 Jul;99(Pt B):281-6. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2015.01.017. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Steroids. 2015. PMID: 25656784 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of antioxidant supplementation on postprandial oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction: a single-blind, 15-day clinical trial in patients with untreated type 2 diabetes, subjects with impaired glucose tolerance, and healthy controls.Clin Ther. 2005 Nov;27(11):1764-73. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.11.006. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 16368447 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Rifampicin, not vitamin E, suppresses parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease development through the pregnane X receptor pathway in piglets.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Jan 1;318(1):G41-G52. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00193.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31604032 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant lipoic acid ligand-shell gold nanoconjugates against oxidative stress caused by α-synuclein aggregates.Nanoscale Adv. 2020 Oct 21;2(12):5666-5681. doi: 10.1039/d0na00688b. eCollection 2020 Dec 15. Nanoscale Adv. 2020. PMID: 36133855 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-proliferative potential and oxidative reactivity of thermo-oxidative degradation products of stigmasterol and stigmasteryl esters for human intestinal cells.Sci Rep. 2023 May 1;13(1):7093. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34335-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37127788 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Concentration of Plant Sterol Oxidation Products (POP) Compared to Cholesterol Oxidation Products (COP) after Intake of Oxidized Plant Sterols: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Dose‒Response Pilot Study.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 30;11(10):2319. doi: 10.3390/nu11102319. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31575059 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety Evaluation of α-Lipoic Acid Supplementation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Studies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 19;9(10):1011. doi: 10.3390/antiox9101011. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33086555 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

