Immunohistochemistry with Anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody is a Sensitive Method for Detection of the BRAF V600E Mutation in Colon Cancer: Evaluation of 120 Cases with and without KRAS Mutation and Literature Review
- PMID: 29127628
- PMCID: PMC6330560
- DOI: 10.1007/s12253-017-0344-x
Immunohistochemistry with Anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody is a Sensitive Method for Detection of the BRAF V600E Mutation in Colon Cancer: Evaluation of 120 Cases with and without KRAS Mutation and Literature Review
Abstract
The major aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) antibody in colorectal tumors with and without KRAS mutation. KRAS and BRAF are two major oncogenic drivers of colorectal cancer (CRC) that have been frequently described as mutually exclusive, thus the BRAF V600E mutation is not expected to be present in the cases with KRAS mutation. In addition, a review of 25 studies comparing immunohistochemistry (IHC) using the anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) antibody with BRAF V600E molecular testing in 4041 patient samples was included. One-hundred and twenty cases with/without KRAS or BRAF mutations were acquired. The tissue were immunostained with anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) antibody with OptiView DAB IHC detection kit. The KRAS mutated cases with equivocal immunostaining were further evaluated by Sanger sequencing for BRAF V600E mutation. Thirty cases with BRAF V600E mutation showed unequivocal, diffuse, uniform, positive cytoplasmic staining and 30 cases with wild-type KRAS and BRAF showed negative staining with anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) antibody. Out of 60 cases with KRAS mutation, 56 cases (93.3%) were negative for BRAF V600E mutation by IHC. Four cases showed weak, equivocal, heterogeneous, cytoplasmic staining along with nuclear staining in 25-90% of tumor cells. These cases were confirmed to be negative for BRAF V600E mutation by Sanger sequencing. Overall, IHC with anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) antibody using recommended protocol with OptiView detection is optimal for detection of BRAF V600E mutation in CRC. Our data are consistent with previous reports indicating that KRAS and BRAF V600E mutation are mutually exclusive.
Keywords: BRAF V600E; Colon cancer; DNA sequencing; Immunohistochemistry; KRAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are employees of Roche Tissue Diagnostics.
Figures
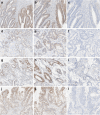
Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemistry using the BRAF V600E mutation-specific monoclonal antibody VE1 is not a useful surrogate for genotyping in colorectal adenocarcinoma.Histopathology. 2013 Aug;63(2):187-93. doi: 10.1111/his.12154. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Histopathology. 2013. PMID: 23763264
-
Ultra-deep sequencing confirms immunohistochemistry as a highly sensitive and specific method for detecting BRAF V600E mutations in colorectal carcinoma.Virchows Arch. 2013 Nov;463(5):623-31. doi: 10.1007/s00428-013-1492-3. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Virchows Arch. 2013. PMID: 24085553
-
BRAFV600E mutation analysis by immunohistochemistry in patients with thoracic metastases from colorectal cancer.Pathology. 2014 Jun;46(4):311-5. doi: 10.1097/PAT.0000000000000113. Pathology. 2014. PMID: 24798160
-
Clinicopathological and molecular features of a large cohort of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and review of the literature: BRAF mutations in KIT/PDGFRA wild-type GISTs are rare events.Hum Pathol. 2017 Apr;62:206-214. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28159677 Review.
-
Comparison of Molecular Methods and BRAF Immunohistochemistry (VE1 Clone) for the Detection of BRAF V600E Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Head Neck Pathol. 2020 Dec;14(4):1067-1079. doi: 10.1007/s12105-020-01166-8. Epub 2020 May 1. Head Neck Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32358715 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative Study of DNA ploidy and BRAF Immunohistochemistry between Colonic Adenocarcinoma and Inflammatory Colonic Lesions.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Apr 1;24(4):1389-1400. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.4.1389. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37116163 Free PMC article.
-
[BRAF-V600E testing in metastatic colorectal cancer and new, chemotherapy-free therapy options. German version].Pathologe. 2021 Nov;42(6):578-590. doi: 10.1007/s00292-021-00942-9. Epub 2021 May 6. Pathologe. 2021. PMID: 33956173 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Coincidence of v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B mutation (V595E) with phosphorylated v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B in urothelial carcinoma in dogs.Can J Vet Res. 2022 Oct;86(4):286-293. Can J Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 36211215 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of hyperuricemia.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Oct;20(4):3292-3300. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10586. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31432190 Free PMC article.
-
ZNF703 is Overexpressed in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Tissues and Mediates K1 Cell Proliferation.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Jan;26(1):355-364. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0494-5. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 30361900
References
-
- Boulagnon C, Dudez O, Beaudoux O, et al. BRAFV600E Gene Mutation in Colonic Adenocarcinomas. Immunohistochemical Detection Using Tissue Microarray and Clinicopathologic Characteristics: An 86 Case Series. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2016;24:88–96. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000157. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

