Two members of the velvet family, VmVeA and VmVelB, affect conidiation, virulence and pectinase expression in Valsa mali
- PMID: 29127722
- PMCID: PMC6638101
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12645
Two members of the velvet family, VmVeA and VmVelB, affect conidiation, virulence and pectinase expression in Valsa mali
Abstract
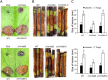
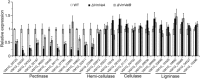
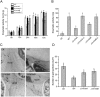
Velvet protein family members are important fungal-specific regulators which are involved in conidial development, secondary metabolism and virulence. To gain a broader insight into the physiological functions of the velvet protein family of Valsa mali, which causes a highly destructive canker disease on apple, we conducted a functional analysis of two velvet protein family members (VmVeA and VmVelB) via a gene replacement strategy. Deletion mutants of VmVeA and VmVelB showed increased melanin production, conidiation and sensitivity to abiotic stresses, but exhibited reduced virulence on detached apple leaves and twigs. Further studies demonstrated that the regulation of conidiation by VmVeA and VmVelB was positively correlated with the melanin synthesis transcription factor VmCmr1. More importantly, transcript levels of pectinase genes were shown to be decreased in deletion mutants compared with those of the wild-type during infection. However, the expression of other cell wall-degrading enzyme genes, including cellulase, hemi-cellulase and ligninase genes, was not affected in the deletion mutants. Furthermore, the determination of pectinase activity and immunogold labelling of pectin demonstrated that the capacity for pectin degradation was attenuated as a result of deletions of VmVeA and VmVelB. Finally, the interaction of VmVeA with VmVelB was identified through co-immunoprecipitation assays. VmVeA and VmVelB play critical roles in conidiation and virulence, probably via the regulation of the melanin synthesis transcription factor VmCmr1 and their effect on pectinase gene expression in V. mali, respectively.
Keywords: Apple Valsa Canker; conidiation; immunogold; melanin accumulation.
© 2017 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A mitogen-activated protein kinase gene (VmPmk1) regulates virulence and cell wall degrading enzyme expression in Valsa mali.Microb Pathog. 2017 Oct;111:298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28888885
-
Gα proteins Gvm2 and Gvm3 regulate vegetative growth, asexual development, and pathogenicityon apple in Valsa mali.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 7;12(3):e0173141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173141. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28267786 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor VmSeb1 is required for the growth, development, and virulence in Valsa mali.Microb Pathog. 2018 Oct;123:132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.06.043. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29959044
-
VmMon1-Ccz1 Complex Is Required for Conidiation, Autophagy, and Virulence in Valsa mali.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2022 Oct;35(10):906-916. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-22-0071-R. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2022. PMID: 35793146
-
Secreted peroxidases VmPODs play critical roles in the conidiation, H2O2 sensitivity and pathogenicity of Valsa mali.Fungal Genet Biol. 2018 Oct;119:20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Fungal Genet Biol. 2018. PMID: 30125671
Cited by
-
Melatonin Treatment Affects Wax Composition and Maintains Storage Quality in 'Kongxin' Plum (Prunus salicina L. cv) during Postharvest.Foods. 2022 Dec 8;11(24):3972. doi: 10.3390/foods11243972. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36553714 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of NADPH oxidases in regulating redox homeostasis and pathogenesis of the poplar canker fungus Cytospora chrysosperma.Stress Biol. 2025 May 8;5(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s44154-025-00223-y. Stress Biol. 2025. PMID: 40338399 Free PMC article.
-
A Velvet Transcription Factor Specifically Activates Mating through a Novel Mating-Responsive Protein in the Human Fungal Pathogen Cryptococcus deneoformans.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0265321. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02653-21. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35471092 Free PMC article.
-
Vm-milR37 contributes to pathogenicity by regulating glutathione peroxidase gene VmGP in Valsa mali.Mol Plant Pathol. 2021 Feb;22(2):243-254. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13023. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Mol Plant Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33278058 Free PMC article.
-
Velvet Family Protein FpVelB Affects Virulence in Association with Secondary Metabolism in Fusarium pseudograminearum.Cells. 2024 May 30;13(11):950. doi: 10.3390/cells13110950. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38891082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghcheh, R.K , Németh, Z. , Atanasova, L. , Fekete, E. , Paholcsek, M. , Sándor, E. , Aquino, B. , Druzhinina, I.S. , Karaffa, L. , and Kubicek, C.P. (2014) The VELVET A orthologue VEL1 of Trichoderma reesei regulates fungal development and is essential for cellulase gene expression. PloS One, 9, e112799. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed, Y.L. , Gerke, J. , Park, H.‐S. , Bayram, Ö. , Neumann, P. , Ni, M. , Dickmanns, A. , Kim, S.C. , Yu, J.‐H. , Braus, G.H. , Ficner, R. and Stock, A.M. (2013) The velvet family of fungal regulators contains a DNA‐binding domain structurally similar to NF‐kappaB. PLoS Biol. 11, e1001750. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bashyal, B.M. , Chand, R. , Kushwaha, C. , Sen, D. , Prasad, L.C. and Joshi, A.K. (2009) Association of melanin content with conidiogenesis in Bipolaris sorokiniana of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26, 309–316.
-
- Bayram, O. and Braus, G.H. (2012) Coordination of secondary metabolism and development in fungi: the velvet family of regulatory proteins. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 36, 1–24. - PubMed
-
- Bayram, O. , Krappmann, S. , Ni, M. , Bok, J.W. , Helmstaedt, K. , Valerius, O. , Braus‐Stromeyer, S. , Kwon, N.J. , Keller, N.P. , Yu, J.H. and Braus, G.H. (2008a) VelB/VeA/LaeA complex coordinates light signal with fungal development and secondary metabolism. Science, 320, 1504–1506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

