Intrathecal administration of antisense oligonucleotide against p38α but not p38β MAP kinase isoform reduces neuropathic and postoperative pain and TLR4-induced pain in male mice
- PMID: 29128611
- PMCID: PMC5940592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.11.007
Intrathecal administration of antisense oligonucleotide against p38α but not p38β MAP kinase isoform reduces neuropathic and postoperative pain and TLR4-induced pain in male mice
Abstract
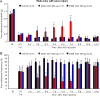
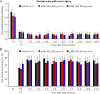
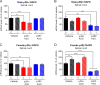
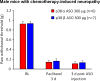
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) consists of two major isoforms: p38α and p38β; however, it remains unclear which isoform is more important for chronic pain development. Recently, we developed potent, long-lasting, and p38 MAPK subtype-specific antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs). We examined the therapeutic effects of isoform-specific ASOs in several chronic pain models following single intrathecal injection (300 μg/10 μl) in CD1 mice. In the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model, p38α MAPK ASO, given on post-operative day 5, reduced CCI-induced mechanical allodynia in male but not female mice. In contrast, mechanical allodynia after CCI in both sexes was not affected by p38β MAPK ASO. Intrathecal injection of p38α or p38β ASO resulted in a partial reduction (≈ 50%) of spinal p38α or p38β mRNA level, respectively, in both sexes at two weeks. In contrast, intrathecal injection of the ASOs did not affect p38α and p38β MAPK mRNA levels in dorsal root ganglia. Intrathecal p38α ASO also reduced postoperative pain (mechanical and cold allodynia) in male mice after tibia fracture. However, intrathecal p38α ASO had no effect on mechanical allodynia in male mice after paclitaxel treatment. Intrathecal p38α MAPK ASO pre-treatment also prevented TLR4-mediated mechanical allodynia and downregulated levels of p38α MAPK and phosphorylated p38 MAPK following intrathecal treatment of lipopolysaccharide. In summary, our findings suggest that p38α MAPK is the major p38 MAPK isoform in the spinal cord and regulates chronic pain in a sex and model-dependent manner. Intrathecal p38α MAPK ASO may offer a new treatment for some chronic pain conditions.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs); Microglia; Neuropathic pain; P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); Sex; Spinal cord.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
BF, AM, HK2 are employees and shareholders of Ionis Pharmaceuticals. However, XL, LZ, NT, RRJ are employees of Duke University and did not receive research fund and compensations from Ionics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spinal p38beta isoform mediates tissue injury-induced hyperalgesia and spinal sensitization.J Neurochem. 2005 Mar;92(6):1508-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02996.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15748168
-
Spinal inhibition of p38 MAP kinase reduces inflammatory and neuropathic pain in male but not female mice: Sex-dependent microglial signaling in the spinal cord.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Jul;55:70-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 26472019 Free PMC article.
-
Role of spinal p38alpha and beta MAPK in inflammatory hyperalgesia and spinal COX-2 expression.Neuroreport. 2010 Mar 10;21(4):313-7. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32833774bf. Neuroreport. 2010. PMID: 20134354 Free PMC article.
-
Leukotrienes in nociceptive pathway and neuropathic/inflammatory pain.Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(8):1163-9. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.1163. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011. PMID: 21804200 Review.
-
p38 MAPK, microglial signaling, and neuropathic pain.Mol Pain. 2007 Nov 1;3:33. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-3-33. Mol Pain. 2007. PMID: 17974036 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolectin B4 (IB4)-conjugated streptavidin for the selective knockdown of proteins in IB4-positive (+) nociceptors.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069241230419. doi: 10.1177/17448069241230419. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 38246917 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 33-mediated inhibition of A-type K+ channels induces sensory neuronal hyperexcitability and nociceptive behaviors in mice.Theranostics. 2022 Feb 14;12(5):2232-2247. doi: 10.7150/thno.69320. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35265208 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates haemorrhage-induced thalamic pain by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/ERK1/2 pathway in mice.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Dec;29(6):1751-1760. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00877-w. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34643849 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in neuroimmune and glial mechanisms of pain.Pain. 2021 Aug 1;162(8):2186-2200. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002215. Pain. 2021. PMID: 34256379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qualitative sex differences in pain processing: emerging evidence of a biased literature.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Jul;21(7):353-365. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0310-6. Epub 2020 May 21. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32440016 Review.
References
-
- Anand P, Shenoy R, Palmer JE, Baines AJ, Lai RYK, Robertson J, Bird N, Ostenfeld T, Chizh BA. Clinical trial of the p38 MAP kinase inhibitor dilmapimod in neuropathic pain following nerve injury. European Journal of Pain. 2011;15:1040–1048. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CF, Swayze EE. RNA Targeting Therapeutics: Molecular Mechanisms of Antisense Oligonucleotides as a Therapeutic Platform. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010;50:259–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

