FGL2 knockdown improves heart function through regulation of TLR9 signaling in the experimental autoimmune myocarditis rats
- PMID: 29128901
- PMCID: PMC11025570
- DOI: 10.1007/s12026-017-8965-4
FGL2 knockdown improves heart function through regulation of TLR9 signaling in the experimental autoimmune myocarditis rats
Abstract
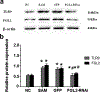
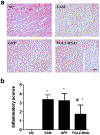
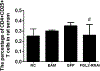
Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (FGL2) is an important immune regulator of both innate and adaptive response. It is present on the surface of macrophages and endothelial cells, and can be constitutively secreted by CD4+CD8+ T cells. Previous studies showed that FGL2 is a potential target for the treatment of experimental autoimmune myocarditis. However, the molecular mechanism of the roles of FGL2 in experimental autoimmune myocarditis is poorly understood. Here, we silenced FGL2 gene by using FGL2-RNAi lentivirus to reveal the heart function in experimental autoimmune myocarditis rats. We found that the cardiac myosin of pigs' hearts induced Lewis rats to come into being as autoimmune myocarditis. TLR9 was upregulated in the heart of experimental autoimmune myocarditis rats. After primary immunization (21 day), the cardiac function of the myocarditis model group improved (P < 0.05). Significantly, the levels of INF-α and NF-κB in the FGL2-RNAi-treated group were lower compared to those in the myocarditis model (EAM) group (P < 0.05). Notably, the inflammation score correspondence with the protein and mRNA levels of TLR9 in myocardial tissues was markedly reduced compared to that in the EAM group (P < 0.05). These results support a role of FGL2 to alleviate inflammatory situation in the myocardium through regulation of the TLR9 signaling pathway in the experimental autoimmune myocarditis rats.
Keywords: Experimental autoimmune myocarditis; Fibrinogen-like protein 2; Toll receptor 9.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
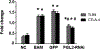
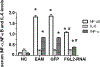
Similar articles
-
Fibrinogen-like protein-2 causes deterioration in cardiac function in experimental autoimmune myocarditis rats through regulation of programmed death-1 and inflammatory cytokines.Immunology. 2018 Feb;153(2):246-252. doi: 10.1111/imm.12837. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Immunology. 2018. PMID: 28892130 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2) on Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) expression in autoimmune myelitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jan;114:109539. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109539. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36508913
-
Contribution of TLR7 and TLR9 signaling to the susceptibility of MyD88-deficient mice to myocarditis.Autoimmunity. 2010 Jun;43(4):275-87. doi: 10.3109/08916930903509056. Autoimmunity. 2010. PMID: 20187710
-
Regulation of inflammation and myocardial fibrosis in experimental autoimmune myocarditis.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2011 Jun;10(3):218-25. doi: 10.2174/187152811795564091. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21495969 Review.
-
The effect of early and late treatment with the tyrphostin AG-556 on the progression of experimental autoimmune myocarditis.Exp Mol Pathol. 2004 Jun;76(3):234-41. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2003.12.011. Exp Mol Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15126106
Cited by
-
FGL2 promotes tumour growth and attenuates infiltration of activated immune cells in melanoma and ovarian cancer models.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 8;14(1):787. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51217-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38191799 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the Rhythm: In Silico Identification of Key Genes and Therapeutic Targets in Atrial Fibrillation.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 25;11(10):2632. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102632. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893006 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of STAT4 Protects Against Autoimmune Myocarditis by Regulating Th1/Th2 Immune Response via Inactivation of the NF-κB Pathway in Rats.Inflammation. 2019 Aug;42(4):1179-1189. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-00978-3. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30848408
References
-
- Zhao P, Sharma AC, Ren J. Pathogenesis and therapy of autoimmunity-induced dilated cardiomyopathy. Front Biosci. 2009;14:1708–15. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe K, Sukumaran V, Veeraveedu PT, Thandavarayan RA, Gurusamy N, Ma M, et al. Regulation of inflammation and myocardial fibrosis in experimental autoimmune myocarditis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2011;10(3):218–25. - PubMed
-
- Shalev I, Wong KM, Foerster K, Zhu Y, Chan C, Maknojia A, et al. The novel CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell effector molecule fibrinogen-like protein 2 contributes to the outcome of murine fulminant viral hepatitis. Hepatology. 2009;49(2):387–97. - PubMed
-
- Han M, Yan W, Guo W, Xi D, Zhou Y, Li W, et al. Hepatitis B virus-induced hFGL-transcription is dependent on c-Ets-2 and MAPK signal pathway[J]. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(47):32715–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

