Hepaprotective Effect of Standardized Ecklonia stolonifera Formulation on CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 29129047
- PMCID: PMC5839501
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2017.199
Hepaprotective Effect of Standardized Ecklonia stolonifera Formulation on CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
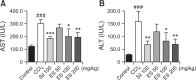
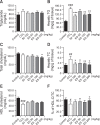
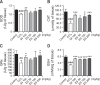
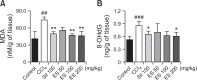
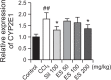
The liver is an essential organ for the detoxification of exogenous xenobiotics, drugs and toxic substances. The incidence rate of non-alcoholic liver injury increases due to dietary habit change and drug use increase. Our previous study demonstrated that Ecklonia stolonifera (ES) formulation has hepatoprotective effect against alcohol-induced liver injury in rat and tacrine-induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cells. This present study was designated to elucidate hepatoprotective effects of ES formulation against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury in Sprague Dawley rat. Sixty rats were randomly divided into six groups. The rats were treated orally with ES formulation and silymarin (served as positive control, only 100 mg/kg/day) at a dose of 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg/day for 21 days. Seven days after treatment, liver injury was induced by intraperitoneal injection of CCl4 (1.5 ml/kg, twice a week for 14 days). The administration of CCl4 exhibited significant elevation of hepatic enzymes (like AST and ALT), and decrease of antioxidant related enzymes (superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase) and glutathione. Then, it leaded to DNA damages (8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine) and lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde). Administration of ES formulation inhibited imbalance of above factors compared to CCl4 induced rat in a dose dependent manner. Real time PCR analysis indicates that CYP2E1 was upregulated in CCl4 induced rat. However, increased gene expression was compromised by ES formulation treatment. These findings suggests that ES formulation could protect hepatotoxicity caused by CCl4 via two pathways: elevation of antioxidant enzymes and normalization of CYP2E1 enzyme.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; CYP2E1; Carbon tetrachloride; Ecklonia stolonifera; Hepatoprotective effect; Non-alcoholic liver injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Fagonia schweinfurthii (Hadidi) Hadidi extract in carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cell line and rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):973-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.048. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24140589
-
In vitro and in vivo antioxidative and hepatoprotective activity of aqueous extract of Cortex Dictamni.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Apr 28;23(16):2912-2927. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.2912. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28522909 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rat is reversed by treatment with riboflavin.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Aug;21(2):383-8. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.05.014. Epub 2014 May 27. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24874442
-
Amomum cardamomum L. ethyl acetate fraction protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury via an antioxidant mechanism in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 May 31;16:155. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1121-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27246748 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of allyl isothiocyanate against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rat.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Jul 25;254:102-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.05.037. Epub 2016 May 27. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 27241356
Cited by
-
In-Depth Understanding of Ecklonia stolonifera Okamura: A Review of Its Bioactivities and Bioactive Compounds.Mar Drugs. 2022 Sep 27;20(10):607. doi: 10.3390/md20100607. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36286432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the antioxidant and protective effects of Marsdenia thyrsiflora Hook.f. leaf extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage in rat models.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 22;15:1463922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1463922. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39502533 Free PMC article.
-
Gold Nanoparticles Using Ecklonia stolonifera Protect Human Dermal Fibroblasts from UVA-Induced Senescence through Inhibiting MMP-1 and MMP-3.Mar Drugs. 2020 Aug 19;18(9):433. doi: 10.3390/md18090433. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32825040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruck R, Aeed H, Avni Y, Shirin H, Matas Z, Shahmurov M, Avinoach I, Zozulya G, Weizman N, Hochman A. Melatonin inhibits nuclear factor κB activation and oxidative stress and protects against thioacetamide induced liver damage in rats. J Hepatol. 2004;40:86–93. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(03)00504-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choi JS, Han YR, Byeon JS, Choung SY, Sohn HS, Jung HA. Protective effect of fucosterol isolated from the edible brown algae, Ecklonia stolonifera and Eisenia bicyclis, on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-and tacrine-induced HepG2 cell injury. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015;67:1170–1178. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12404. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

