Genetic Predisposition, Clinical Risk Factor Burden, and Lifetime Risk of Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 29129827
- PMCID: PMC5840011
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031431
Genetic Predisposition, Clinical Risk Factor Burden, and Lifetime Risk of Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
Background: The long-term probability of developing atrial fibrillation (AF) considering genetic predisposition and clinical risk factor burden is unknown.
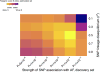
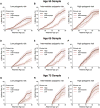
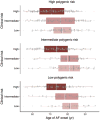
Methods: We estimated the lifetime risk of AF in individuals from the community-based Framingham Heart Study. Polygenic risk for AF was derived using a score of ≈1000 AF-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Clinical risk factor burden was calculated for each individual using a validated risk score for incident AF comprised of height, weight, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, current smoking status, antihypertensive medication use, diabetes mellitus, history of myocardial infarction, and history of heart failure. We estimated the lifetime risk of AF within tertiles of polygenic and clinical risk.
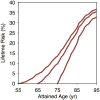
Results: Among 4606 participants without AF at 55 years of age, 580 developed incident AF (median follow-up, 9.4 years; 25th-75th percentile, 4.4-14.3 years). The lifetime risk of AF >55 years of age was 37.1% and was substantially influenced by both polygenic and clinical risk factor burden. Among individuals free of AF at 55 years of age, those in low-polygenic and clinical risk tertiles had a lifetime risk of AF of 22.3% (95% confidence interval, 15.4-9.1), whereas those in high-risk tertiles had a risk of 48.2% (95% confidence interval, 41.3-55.1). A lower clinical risk factor burden was associated with later AF onset after adjusting for genetic predisposition (P<0.001).
Conclusions: In our community-based cohort, the lifetime risk of AF was 37%. Estimation of polygenic AF risk is feasible and together with clinical risk factor burden explains a substantial gradient in long-term AF risk.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; epidemiology; genetics; lifetime risk; polygenic risk; risk factor; risk stratification.
© 2018 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Arnar DO, Thorvaldsson S, Manolio TA, Thorgeirsson G, Kristjansson K, Hakonarson H, Stefansson K. Familial aggregation of atrial fibrillation in Iceland. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:708–712. - PubMed
-
- Alonso A, Krijthe BP, Aspelund T, Stepas KA, Pencina MJ, Moser CB, Sinner MF, Sotoodehnia N, Fontes JD, Janssens AC, Kronmal RA, Magnani JW, Witteman JC, Chamberlain AM, Lubitz SA, Schnabel RB, Agarwal SK, McManus DD, Ellinor PT, Larson MG, Burke GL, Launer LJ, Hofman A, Levy D, Gottdiener JS, Kaab S, Couper D, Harris TB, Soliman EZ, Stricker BH, Gudnason V, Heckbert SR, Benjamin EJ. Simple Risk Model Predicts Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation in a Racially and Geographically Diverse Population: the CHARGE-AF Consortium. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e000102. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Christophersen IE, Rienstra M, Roselli C, Yin X, Geelhoed B, Barnard J, Lin H, Arking DE, Smith AV, Albert CM, Chaffin M, Tucker NR, Li M, Klarin D, Bihlmeyer NA, Low SK, Weeke PE, Muller-Nurasyid M, Smith JG, Brody JA, Niemeijer MN, Dorr M, Trompet S, Huffman J, Gustafsson S, Schurmann C, Kleber ME, Lyytikainen LP, Seppala I, Malik R, Horimoto A, Perez M, Sinisalo J, Aeschbacher S, Theriault S, Yao J, Radmanesh F, Weiss S, Teumer A, Choi SH, Weng LC, Clauss S, Deo R, Rader DJ, Shah SH, Sun A, Hopewell JC, Debette S, Chauhan G, Yang Q, Worrall BB, Pare G, Kamatani Y, Hagemeijer YP, Verweij N, Siland JE, Kubo M, Smith JD, Van Wagoner DR, Bis JC, Perz S, Psaty BM, Ridker PM, Magnani JW, Harris TB, Launer LJ, Shoemaker MB, Padmanabhan S, Haessler J, Bartz TM, Waldenberger M, Lichtner P, Arendt M, Krieger JE, Kahonen M, Risch L, Mansur AJ, Peters A, Smith BH, Lind L, Scott SA, Lu Y, Bottinger EB, Hernesniemi J, Lindgren CM, Wong JA, Huang J, Eskola M, Morris AP, Ford I, Reiner AP, Delgado G, Chen LY, Chen YI, Sandhu RK, Li M, Boerwinkle E, Eisele L, Lannfelt L, Rost N, Anderson CD, Taylor KD, Campbell A, Magnusson PK, Porteous D, Hocking LJ, Vlachopoulou E, Pedersen NL, Nikus K, Orho-Melander M, Hamsten A, Heeringa J, Denny JC, Kriebel J, Darbar D, Newton-Cheh C, Shaffer C, Macfarlane PW, Heilmann-Heimbach S, Almgren P, Huang PL, Sotoodehnia N, Soliman EZ, Uitterlinden AG, Hofman A, Franco OH, Volker U, Jockel KH, Sinner MF, Lin HJ, Guo X, ISGC MCot, Neurology Working Group of the CC. Dichgans M, Ingelsson E, Kooperberg C, Melander O, Loos RJF, Laurikka J, Conen D, Rosand J, van der Harst P, Lokki ML, Kathiresan S, Pereira A, Jukema JW, Hayward C, Rotter JI, Marz W, Lehtimaki T, Stricker BH, Chung MK, Felix SB, Gudnason V, Alonso A, Roden DM, Kaab S, Chasman DI, Heckbert SR, Benjamin EJ, Tanaka T, Lunetta KL, Lubitz SA, Ellinor PT, Consortium AF. Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet. 2017;49:946–952. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Low SK, Takahashi A, Ebana Y, Ozaki K, Christophersen IE, Ellinor PT, Consortium AF, Ogishima S, Yamamoto M, Satoh M, Sasaki M, Yamaji T, Iwasaki M, Tsugane S, Tanaka K, Naito M, Wakai K, Tanaka H, Furukawa T, Kubo M, Ito K, Kamatani Y, Tanaka T. Identification of six new genetic loci associated with atrial fibrillation in the Japanese population. Nat Genet. 2017;49:953–958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

