Lipoquality control by phospholipase A2 enzymes
- PMID: 29129849
- PMCID: PMC5743847
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.93.043
Lipoquality control by phospholipase A2 enzymes
Abstract
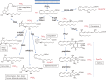
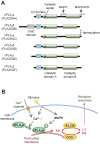
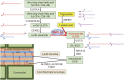
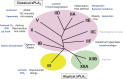
The phospholipase A2 (PLA2) family comprises a group of lipolytic enzymes that typically hydrolyze the sn-2 position of glycerophospholipids to give rise to fatty acids and lysophospholipids. The mammalian genome encodes more than 50 PLA2s or related enzymes, which are classified into several subfamilies on the basis of their structures and functions. From a general viewpoint, the PLA2 family has mainly been implicated in signal transduction, producing bioactive lipid mediators derived from fatty acids and lysophospholipids. Recent evidence indicates that PLA2s also contribute to phospholipid remodeling for membrane homeostasis or energy production for fatty acid β-oxidation. Accordingly, PLA2 enzymes can be regarded as one of the key regulators of the quality of lipids, which I herein refer to as lipoquality. Disturbance of PLA2-regulated lipoquality hampers tissue and cellular homeostasis and can be linked to various diseases. Here I overview the current state of understanding of the classification, enzymatic properties, and physiological functions of the PLA2 family.
Keywords: fatty acid; lipid; lipidomics; membrane; phospholipase; phospholipid.
Figures



References
-
- Shimizu T. (2009) Lipid mediators in health and disease: enzymes and receptors as therapeutic targets for the regulation of immunity and inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 49, 123–150. - PubMed
-
- Narumiya S., Furuyashiki T. (2011) Fever, inflammation, pain and beyond: prostanoid receptor research during these 25 years. FASEB J. 25, 813–818. - PubMed
-
- Aikawa S., Hashimoto T., Kano K., Aoki J. (2015) Lysophosphatidic acid as a lipid mediator with multiple biological actions. J. Biochem. 157, 81–89. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto K., Miki Y., Sato H., Murase R., Taketomi Y., Murakami M. (2017) Secreted phospholipase A2 specificity on natural membrane phospholipids. Methods Enzymol. 583, 101–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

