Successful Pelvic Resection for Acetabular Hydatidosis
- PMID: 29130011
- PMCID: PMC5654322
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9495783
Successful Pelvic Resection for Acetabular Hydatidosis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Successful Pelvic Resection for Acetabular Hydatidosis".Case Rep Orthop. 2019 Sep 4;2019:2942858. doi: 10.1155/2019/2942858. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Orthop. 2019. PMID: 31565454 Free PMC article.
Abstract
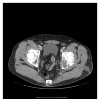
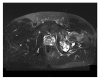
Background: Hydatidosis of the bone is a rare occurrence (0.9 to 2.5% of all localization of the disease). In those occurrences, the pelvic bone is the second most frequent localization. Curative treatment of pelvic bone hydatidosis is difficult and a consensus is yet to be found.
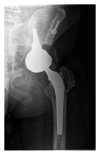
Clinical case: We report a case of hydatidosis of the ischium, extended to the homolateral hip. The patient was treated through hip resection using patient-specific cutting guides, followed by total hip reconstruction. Albendazole was administered to the patient for two months before the surgery and for three months following the surgery.
Conclusions: In a young patient, hydatidosis of the pelvic bone can be treated with satisfying results through wide resection of the hip coupled with an antiparasitic treatment administered before and after the surgery. Prosthetic reconstruction, similar to what is done in cancer surgery, restores good functions.
Figures
References
-
- Zlitni M., Ezzaouia K., Bouzidi R., Lebib H., Mestiri M., Kooli M. Manifestations osseuses des parasitoses. EMC - Appareil locomoteur. 2009;4(3):1–9. doi: 10.1016/S0246-0521(09)44800-9. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources