The PDZ-Binding Motif of HPV16-E6 Oncoprotein Modulates the Keratinization and Stemness Transcriptional Profile In Vivo
- PMID: 29130045
- PMCID: PMC5654334
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7868645
The PDZ-Binding Motif of HPV16-E6 Oncoprotein Modulates the Keratinization and Stemness Transcriptional Profile In Vivo
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this work was to compare the early gene expression profiles in the skin of HPV16-E6 transgenic mice regulated by the E6 PDZ-binding motif.
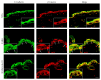
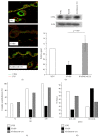
Materials and methods: The global transcriptional profiles in dorsal skin biopsies from K14E6 and K14E6Δ146-151 transgenic mice were compared using microarrays. Relevant genes obtained from the most differentially expressed processes were further examined by RT-qPCR, in situ RT-PCR, Western blot, or immunofluorescence.
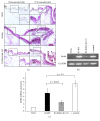
Results: The transcriptomic landscape of K14E6 versus K14E6Δ146-151 shows that the most affected expression profiles were those related to keratinocyte differentiation, stem cell maintenance, and keratinization. Additionally, downregulation of epidermal stemness markers such as K15 and CD34, as well as the upregulation of cytokeratin 6b, appeared to be dependent on the E6 PDZ-binding motif. Finally, wound healing, a physiological process linked to stemness, is impaired in the K14E6 mice compared to K14E6Δ146-151.
Conclusion: The E6 PDZ-binding motif appears to affect stemness and keratinization during early stages of skin carcinogenesis. As E6 plays a significant role in HPV-induced skin carcinogenesis, the K14E6 versus K14E6Δ146-151 transcriptional profile provides a source of valuable data to uncover novel E6 functions in the skin.
Figures

References
-
- Pfister H. Chapter 8: Human papillomavirus and skin cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Monographs. 2003;(31):52–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

