Models of spatial and temporal dimensions of memory
- PMID: 29130060
- PMCID: PMC5675108
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2017.05.024
Models of spatial and temporal dimensions of memory
Abstract
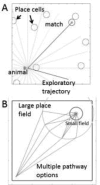
Episodic memory involves coding of the spatial location and time of individual events. Coding of space and time is also relevant to working memory, spatial navigation, and the disambiguation of overlapping memory representations. Neurophysiological data demonstrate that neuronal activity codes the current, past and future location of an animal as well as temporal intervals within a task. Models have addressed how neural coding of space and time for memory function could arise, with both dimensions coded by the same neurons. Neural coding could depend upon network oscillatory and attractor dynamics as well as modulation of neuronal intrinsic properties. These models are relevant to the coding of space and time involving structures including the hippocampus, entorhinal cortex, retrosplenial cortex, striatum and parahippocampal gyrus, which have been implicated in both animal and human studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Brown TI, Stern CE. Contributions of medial temporal lobe and striatal memory systems to learning and retrieving overlapping spatial memories. Cereb Cortex. 2014;24:1906–1922. Study showing fMRI activation in the hippocampus when viewing the initial location of an overlapping trajectory and retrieving the full trajectory to generate a correct response. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown TI, Carr VA, LaRocque KF, Favila SE, Gordon AM, Bowles B, Bailenson JN, Wagner AD. Prospective representation of navigational goals in the human hippocampus. Science. 2016;352:1323–1326. Multi-voxel pattern analysis of fMRI data showing that retrieval of a trajectory to a different location on a circular pathway involves reactivation of the representation of intermediate locations along that trajectory. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
