Tumor molecular profiling of NSCLC patients using next generation sequencing
- PMID: 29130105
- PMCID: PMC5783588
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2017.6051
Tumor molecular profiling of NSCLC patients using next generation sequencing
Abstract
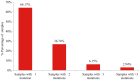
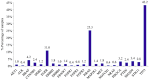
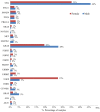
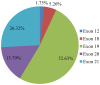
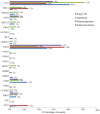
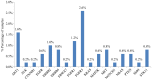
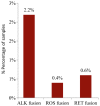
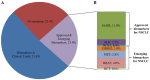
Non‑small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer and a tumor with a broad spectrum of targeted therapies already available or in clinical trials. Thus, molecular characterization of the tumor using next generation sequencing (NGS) technology, has become a key tool for facilitating treatment decisions and the clinical management of NSCLC patients. The performance of a custom 23 gene multiplex amplification hot spot panel, based on Ion AmpliSeq™ technology, was evaluated for the analysis of tumor DNA extracted from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues. Furthermore, the Ion AmpliSeq™ RNA Fusion Lung Cancer Research Panel was used for fusion RNA transcript analysis. The mutation spectrum of the tumors was determined in a cohort of 502 patients with NSCLC using the aforementioned targeted gene panels. The panel used for tumor DNA analysis in this study exhibited high rates (100%) of sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility at a mutation allelic frequency of 3%. At least one DNA mutation was detected in 374 patients (74.5%) and an RNA fusion was identified in 16 patients, (3.2%). In total, alterations in a cancer-driver gene were identified (including point mutations, gene rearrangements and MET amplifications) in 77.6% of the tumors tested. Among the NSCLC patients, 23% presented a mutation in a gene associated with approved or emerging targeted therapy. More specifically, 13.5% (68/502) presented a mutation in a gene with approved targeted therapy (EGFR, ALK, ROS1) and 9.4% (47/502) had an alteration in a gene related to emerging targeted therapies (ERBB2, BRAF, MET and RET). Furthermore, 51.6% of the patients had a mutation in a gene that could be related to an off label therapy or indicative for access to a clinical trial. Thus, the targeted NGS panel used in this study is a reliable approach for tumor molecular profiling and can be applied in personalized treatment decision making for NSCLC patients.
Figures
References
-
- Diaz Z, Aguilar-Mahecha A, Paquet ER, Basik M, Orain M, Camlioglu E, Constantin A, Benlimame N, Bachvarov D, Jannot G, et al. Next-generation biobanking of metastases to enable multidimensional molecular profiling in personalized medicine. Mod Pathol. 2013;26:1413–1424. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.81. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

