Animal Models for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Studies
- PMID: 29130177
- PMCID: PMC6538071
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7309-5_18
Animal Models for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Studies
Abstract
Quorum sensing (QS) systems play global regulatory roles in bacterial virulence. They synchronize the expression of multiple virulence factors and they control and modulate bacterial antibiotic tolerance systems and host defense mechanisms. Therefore, it is important to obtain knowledge about QS modes of action and to test putative therapeutics that may interrupt QS actions in the context of infections. This chapter describes methods to study bacterial pathogenesis in murine acute and persistent/relapsing infection models, using the Gram-negative bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa as an example. These infection models can be used to probe bacterial virulence functions and in mechanistic studies, as well as for the assessment of the therapeutic potential of antibacterials, including anti-virulence agents.
Keywords: Abdominal burn infection; Antibiotic tolerance; Back burn infection; Lung infection; Open wound infection; Persistence; Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Figures
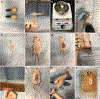

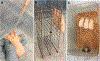
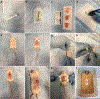
References
-
- Gellatly SL, Hancock RE (2013) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: new insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathog Dis 67:159–173 - PubMed
-
- Kerr KG, Snelling AM (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a formidable and ever-present adversary. J Hosp Infect 73:338–344 - PubMed
-
- Crouch Brewer S, Wunderink RG, Jones CB, Leeper KV Jr (1996) Ventilator-associated pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chest 109:1019–1029 - PubMed
-
- Pier GB, Ramphal R (2004) Pseudomonas aeruginosa In: Mandell GL, Bennet JE, Dolin R (eds) Principles and practise of infectious diseases, vol 6 Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 2587–2615
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

