Association between plasma fibrinogen and survival in patients with small-cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 29131503
- PMCID: PMC5754299
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12556
Association between plasma fibrinogen and survival in patients with small-cell lung carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Elevated plasma fibrinogen (Fbg) levels contribute to tumor progression and metastasis; however, limited research on Fbg in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) has been conducted. This study evaluated the prognostic value of Fbg levels in patients with SCLC.
Methods: Data on plasma Fbg level, clinical features, and overall survival were retrospectively collected. Kaplan-Meier estimates and log-rank tests were used to analyze the relationship between Fbg level and survival. Multivariate analyses were performed to determine independent prognostic factors. Subgroup analyses were performed based on extensive/limited disease and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group status.
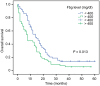
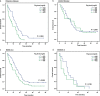
Results: A total of 120 patients with SCLC were included. The one, three, and five-year survival rates for the entire cohort were 48.3%, 9.2%, and 1.7%, respectively. Univariate analyses revealed that age, alcohol use, clinical stage, pleural effusion, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group grade, and Fbg and lactate dehydrogenase levels were associated with survival (P < 0.05). The median survival time for patients with high Fbg levels (> 400 mg/dL) was shorter than for those with low Fbg levels (8 vs. 14 months; P = 0.013). Furthermore, multivariate analysis revealed that Fbg was negatively and independently associated with SCLC prognosis (hazard ratio 1.505, 95% confidence interval 1.018-2.226; P = 0.041). Higher Fbg levels were associated with shorter survival in the extensive disease subgroup (7 vs. 12 months; P = 0.004).
Conclusions: Elevated plasma Fbg was an independent factor associated with poor outcomes in SCLC patients and could serve as a prognostic biomarker.
Keywords: Fibrinogen; prognosis; small-cell lung carcinoma; survival.
© 2017 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016; 66: 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Oh JR, Seo JH, Hong CM et al Extra‐thoracic tumor burden but not thoracic tumor burden on (18)F‐FDG PET/CT is an independent prognostic biomarker for extensive‐disease small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2013; 81: 218–25. - PubMed
-
- Polterauer S, Seebacher V, Hefler‐Frischmuth K et al Fibrinogen plasma levels are an independent prognostic parameter in patients with cervical cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200 (647): e1–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

