Exemplar Variability Facilitates Retention of Word Learning by Children With Specific Language Impairment
- PMID: 29131888
- PMCID: PMC6105085
- DOI: 10.1044/2017_LSHSS-17-0031
Exemplar Variability Facilitates Retention of Word Learning by Children With Specific Language Impairment
Abstract
Purpose: Variability in the input plays an important role in language learning. The current study examined the role of object variability for new word learning by preschoolers with specific language impairment (SLI).
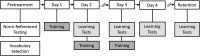
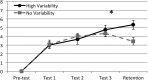
Method: Eighteen 4- and 5-year-old children with SLI were taught 8 new words in 3 short activities over the course of 3 sessions. Half of the children saw 3 identical objects corresponding to each new word during training (No Variability group); the other half of the children saw 3 different objects corresponding to each new word during training (High Variability group). Children completed vocabulary learning tests for objects seen during training and for new within-category objects that were never seen during training as a test of category generalization. Learning was assessed the day after each training activity, and retention was assessed 3 weeks after the last training session.
Results: There were no group differences on trained or generalization items immediately following training sessions. However, children in the High Variability group demonstrated significantly better retention 3 weeks after experimental training.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that object variability facilitates retention of new word learning by children with SLI.
Supplemental material: https://doi.org/10.23641/asha.5583979.
Figures

References
-
- Aguilar J. M., & Plante E. (2014). Learning of grammar-like visual sequences by adults with and without language-learning disabilities. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 57, 1394–1404. - PubMed
-
- Alt M., Meyers C., & Ancharski A. (2012). Using principles of learning to inform language therapy design for children with specific language impairment. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 47, 487–498. - PubMed
-
- Alt M., & Plante E. (2006). Factors that influence lexical and semantic fast mapping of young children with specific language impairment. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 49, 941–954. - PubMed
-
- Alt M., Plante E., & Creusere M. (2004). Semantic features in fast-mapping performance of preschoolers with specific language impairment versus preschoolers with normal language. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 47(2), 407–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

