Avian infectious bronchitis virus disrupts the melanoma differentiation associated gene 5 (MDA5) signaling pathway by cleavage of the adaptor protein MAVS
- PMID: 29132350
- PMCID: PMC5683607
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-017-1253-7
Avian infectious bronchitis virus disrupts the melanoma differentiation associated gene 5 (MDA5) signaling pathway by cleavage of the adaptor protein MAVS
Abstract
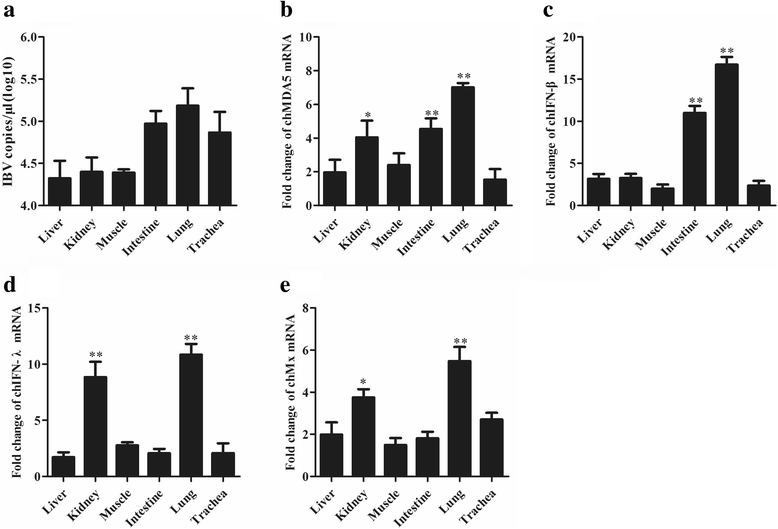
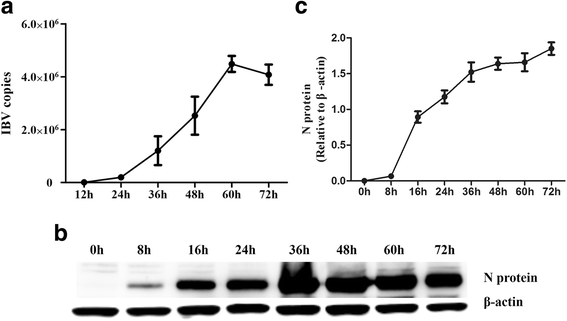
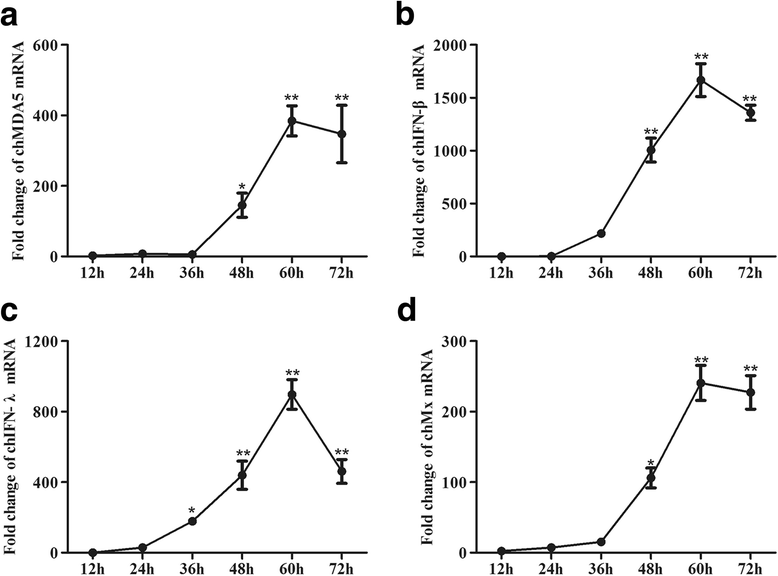
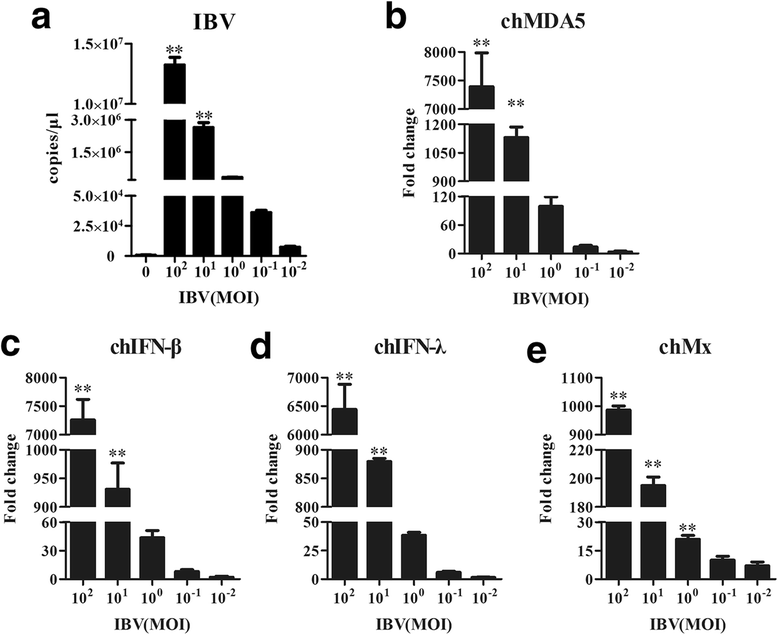
Background: Melanoma differentiation associated gene 5 (MDA5) and retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) selectively sense cytoplasmic viral RNA to induce an antiviral immune response. Infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) is one of the most important infectious agents in chickens, and in chicken cells, it can be recognized by MDA5 to activate interferon production. RIG-I is considered to be absent in chickens. However, the absence of RIG-I in chickens raises the question of whether this protein influences the antiviral immune response against IBV infection.
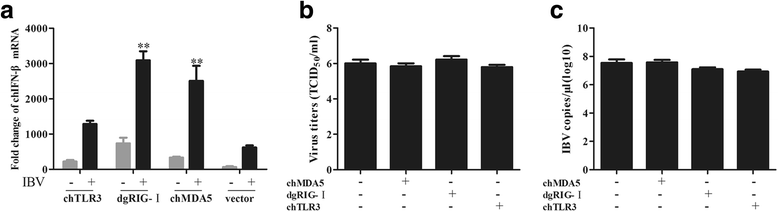
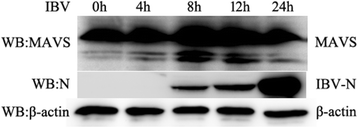
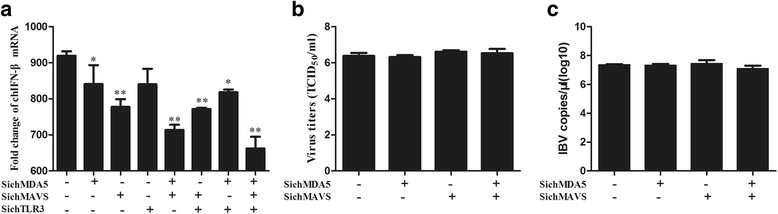
Results: Here, we showed that chicken cells transfected with domestic goose RIG-I (dgRIG-I) exhibited increased IFN-β activity after IBV infection. We also found that IBV can cleave MAVS, an adaptor protein downstream of RIG-I and MDA5 that acts as a platform for antiviral innate immunity at an early stage of infection.
Conclusions: Although chicken MDA5 (chMDA5) is functionally active during IBV infection, the absence of RIG-I may increase the susceptibility of chickens to IBV infection, and IBV may disrupt the activation of the host antiviral response through the cleavage of MAVS.
Keywords: Infectious bronchitis virus; Mavs; Melanoma differentiation associated gene 5; Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Jiangsu Administrative Committee for Laboratory Animals approved all animal studies (Permit number: SYXKSU-2007-0005) according to the guidelines of Jiangsu Laboratory Animal Welfare and Ethical of Jiangsu Administrative Committee of Laboratory Animals.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Kint J, Dickhout A, Kutter J, Maier HJ, Britton P, Koumans J, Pijlman GP, Fros JJ, Wiegertjes GF, Forlenza M. Infectious bronchitis Coronavirus inhibits STAT1 signaling and requires accessory proteins for resistance to type I interferon activity. J Virol. 2015;89(23):12047–12057. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01057-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kint J, Langereis MA, Maier HJ, Britton P, van Kuppeveld FJ, Koumans J, Wiegertjes GF, Forlenza M. Infectious bronchitis Coronavirus limits interferon production by inducing a host shutoff that requires accessory protein 5b. J Virol. 2016;90(16):7519–7528. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00627-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

