Therapeutic efficacy of pentoxifylline on proteinuria and renal progression: an update
- PMID: 29132351
- PMCID: PMC5683556
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-017-0390-4
Therapeutic efficacy of pentoxifylline on proteinuria and renal progression: an update
Abstract
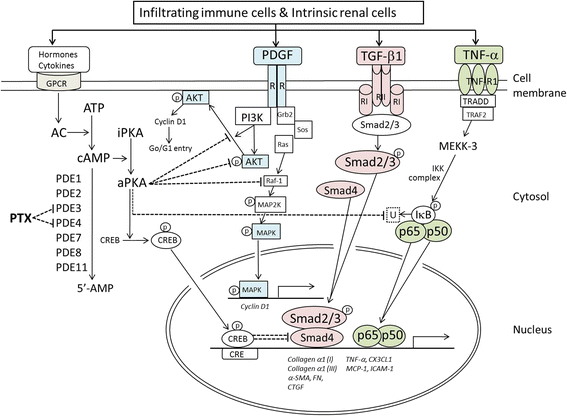
Blood pressure control with renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade has remained the gold standard for treating patients with proteinuric chronic kidney disease (CKD) up to date. Nevertheless, RAS blockade slows but does not halt the progression of kidney disease, thus highlighting the need to search for additional therapeutic approaches. The nonselective phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor pentoxifylline (PTX) is an old drug that exhibits prominent anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-fibrotic activities both in vitro and in vivo. Studies in human subjects have shown that PTX monotherapy decreases urinary protein excretion, and add-on therapy of PTX to background RAS blockade additively reduces proteinuria in patients with CKD of various etiology. More recent studies find that PTX combined with RAS blockade delays the decline of glomerular filtration rate in diabetic patients with mild to moderate CKD, and reduces the risk of end-stage renal disease in diabetic and non-diabetic patients in late stage of CKD with high proteinuria levels. In this review, we update the clinical trial results of PTX as monotherapy, or in conjunction or in comparison with RAS blockade on patients with proteinuria and CKD, and propose a mechanistic scheme explaining the renoprotective activities of this drug.
Keywords: CKD; ESRD; Pentoxifylline; Proteinuria; Renin-angiotensin system.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
None.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Kidney Disease Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) blood pressure work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. Kidney inter, Suppl. 2012;2:337–414. doi: 10.1038/kisup.2012.46. - DOI
-
- Kidney Disease Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) CKD work group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney inter., Suppl. 2013;3:1–150. doi: 10.1038/kisup.2012.73. - DOI
-
- Taiwan chronic kidney clinical guidelines 2015. http://www.tsn.org.tw/UI/H/H00202.aspx [Article in Chinese].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

