Hepatitis B virus inhibits the in vivo and in vitro synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein C3
- PMID: 29132372
- PMCID: PMC5683573
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0607-2
Hepatitis B virus inhibits the in vivo and in vitro synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein C3
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in the body can damage liver cells and cause disorders in blood lipid metabolism. Apolipoprotein C3 (ApoC3) plays an important role in the regulation of lipid metabolism, but no study on the HBV regulation of ApoC3 has been reported. This purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of HBV on ApoC3 expression and its regulatory mechanism.
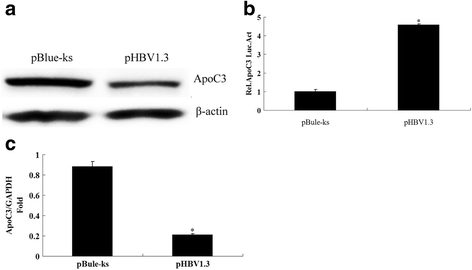
Methods: The expression levels of ApoC3 mRNA and protein in the human hepatoma cell lines HepG2 and HepG2.2.15 were determined using real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blot. The HepG2 cells were co-transfected with the ApoC3 gene promoter and either HBV-infected clone pHBV1.3 or its individual genes. The changes in luciferase activity were assayed. The expression levels of ApoC3 mRNA and protein were determined using RT-qPCR and Western blot. The content of ApoC3 in the supernatant of the cultured cells was determined using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The sera were collected from 149 patients with HBV infection and 102 healthy subjects at physical examination as the normal controls. The serological levels of ApoC3 in the HBV group and the normal control group were determined using ELISA. The contents of serum triglyceride (TG) and very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) in the HBV patients and the normal control were determined using an automatic biochemical analyser.
Results: The expression levels of ApoC3 mRNA and protein were lower in the HepG2.2.15 cells than in the HepG2 cells. pHBV1.3 and its X gene could inhibit the activity of the ApoC3 promoter and its mRNA and protein expression. The serum levels of ApoC3, VLDL and TG were 65.39 ± 7.48 μg/ml, 1.24 ± 0.49 mmol/L, and 0.46 ± 0.10 mmol/L in the HBV patients and 41.02 ± 6.88 μg/ml, 0.76 ± 0.21 mmol/L, 0.29 ± 0.05 mmol/L in the normal controls, respectively, statistical analysis revealed significantly lower serum levels of ApoC3, VLDL and TG in HBV patients than in the normal controls (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: HBV can inhibit the in vivo and in vitro synthesis and secretion of ApoC3.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein C3; Hepatitis B virus; Triglyceride; Very-low-density lipoprotein.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Wuhan University People’s Hospital, and all subjects signed the informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mechanism of apoliprotein A1 down-regulated by Hepatitis B virus.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Mar 25;15:64. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0232-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27015844 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus inhibits apolipoprotein A5 expression through its core gene.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Oct 10;15(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0340-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27724895 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting effect of hepatitis B virus on the expressoin of phospholipase A2 group IIA.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Jan 11;16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0400-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28077172 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Role of Apolipoprotein C3 in Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Metabolic Disorder in Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 27;25(23):12759. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312759. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein C3: form begets function.J Lipid Res. 2024 Jan;65(1):100475. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2023.100475. Epub 2023 Nov 14. J Lipid Res. 2024. PMID: 37972731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum apolipoprotein C3 levels are negatively associated with hepatitis B virus DNA in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Jun 11;18(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1084-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31186008 Free PMC article.
-
Small hepatitis B virus surface antigen (SHBs) induces dyslipidemia by suppressing apolipoprotein-AII expression through ER stress-mediated modulation of HNF4α and C/EBPγ.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0123924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01239-24. Epub 2024 Oct 29. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39470210 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Interaction Between Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Lipid Metabolism in Hepatocytes: A Potential Target of Antiviral Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 11;12:636897. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.636897. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33776969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin resistance exhibits varied metabolic abnormalities in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, chronic hepatitis B and the combination of the two: a cross-sectional study.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019 Jun 15;11:45. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0440-z. eCollection 2019. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31223344 Free PMC article.
-
Transaminase Elevations during Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: Safety Considerations and Role in Achieving Functional Cure.Viruses. 2021 Apr 23;13(5):745. doi: 10.3390/v13050745. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33922828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No.PKJ2016-Y56/Pudong New Area Science and Technology Development Fund
- ZK2015B16/the key specialty construction Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau
- 81672079, 30973073, 81172042/the National Science Foundation of China
- 2016KF003/the Open Research Program of the State Key Laboratory of Virology of China
- PWZxq2017-15/the Disciplines Group Construction Project of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

